A loss function is a method of evaluating how well your machine learning algorithm models your featured data set. In other words, loss functions are a measurement of how good your model is at predicting outcomes.
What Are Loss Functions in Machine Learning?
A loss function (or error function) in machine learning is a mathematical function that measures the difference between a model’s predicted outputs and the actual target values of a featured data set.
In machine learning, a loss function measures error for a single training example, while a cost function aggregates the loss across all training examples (often as an average). In some contexts, the cost function may also include regularization terms. We calculate the cost function as the average of all loss function values, whereas we calculate the loss function for each sample output compared to its actual value.
The loss function is directly related to the predictions of the model you’ve built. If your loss function value is low, your model will provide good results. The loss function (or rather, the cost function) you use to evaluate the model performance needs to be minimized to improve its performance.
Types of Loss Functions
Broadly speaking, loss functions can be grouped into two major categories concerning the types of problems we come across in the real world: classification and regression.
In classification problems, our task is to predict the respective probabilities of all classes the problem is dealing with.
On the other hand, when it comes to regression, our task is to predict the continuous value concerning a given set of independent features to the learning algorithm.
Assumptions of Loss Functions
- n/m — number of training samples
- i — ith training sample in a data set
- y(i) — Actual value for the ith training sample
- ŷ(i) — Predicted value for the ith training sample
Loss Functions for Classification
1. Binary Cross-Entropy Loss / Log Loss
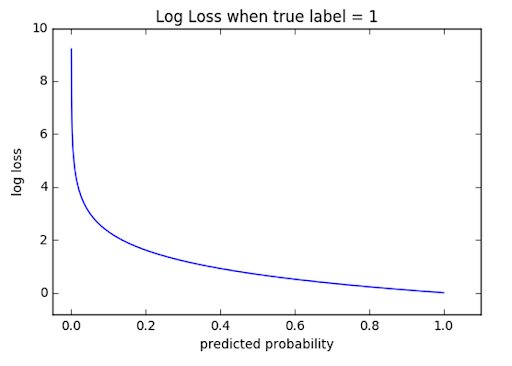
This is the most common loss function used in classification problems. The cross-entropy loss decreases as the predicted probability converges to the actual label. It measures the performance of a classification model whose predicted output is a probability value between 0 and 1.
When the number of classes is 2, it’s binary classification.
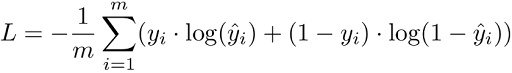
When the number of classes is more than 2, it’s multi-class classification.
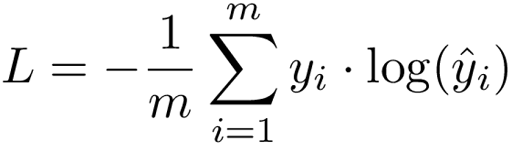
We derive the cross-entropy loss formula from the regular likelihood function, but with logarithms added in.
Binary cross-entropy is used for two-class problems, while categorical cross-entropy is used for multi-class classification.
2. Hinge Loss
The second most common loss function used for classification problems and an alternative to the cross-entropy loss function is hinge loss, primarily developed for support vector machine (SVM) model evaluation.
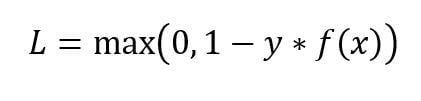
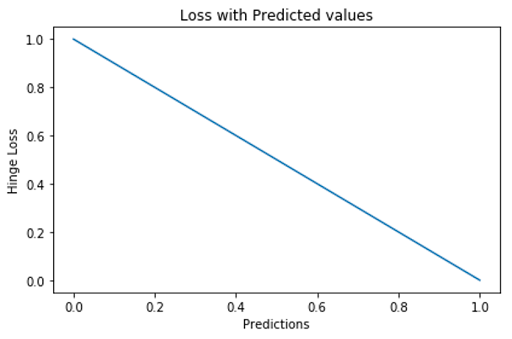
Hinge loss penalizes the wrong predictions and the right predictions that are not confident. It requires labels to be -1 and 1, rather than 0 and 1. Hinge loss is primarily used with SVM classifiers with class labels as -1 and 1.
Loss Functions for Regression
1. Mean Squared Error / Quadratic Loss / L2 Loss
We define the mean squared error (MSE) loss function, or L2 loss, as the average of squared differences between the actual value (Y) and the predicted value (Ŷ). It’s the most commonly used regression loss function.
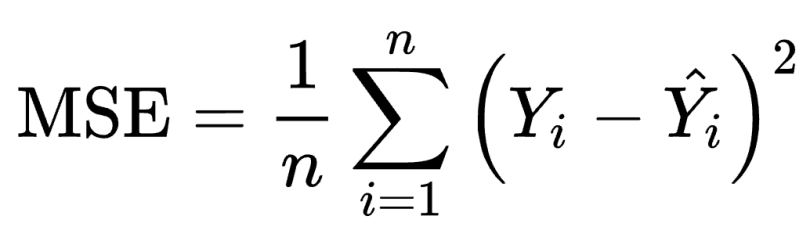
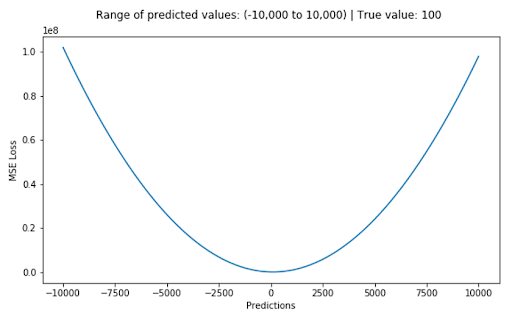
The corresponding cost function is the mean of these squared errors (MSE). The MSE loss function penalizes the model for making large errors by squaring them,making the MSE cost function less robust to outliers. Therefore, you shouldn’t use it if the data is prone to many outliers.
2. Mean Absolute Error / L1 Loss
We define the mean absolute error (MAE) loss function, or L1 loss, as the average of absolute differences between the actual and the predicted value. It’s the second most commonly used regression loss function. It measures the average magnitude of errors in a set of predictions, without considering their directions.
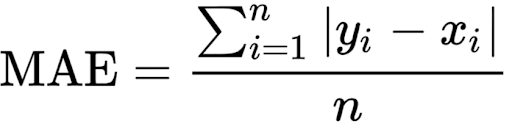
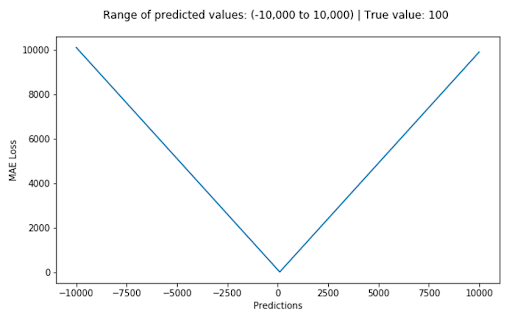
The corresponding cost function is the mean of these absolute errors (MAE). The MAE loss function is more robust to outliers compared to the MSE loss function. Therefore, you should use it if the data is prone to many outliers.
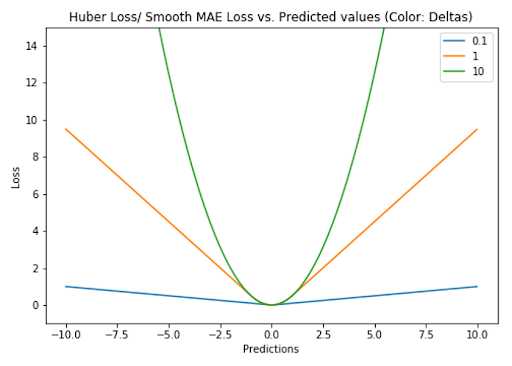
3. Huber Loss / Smooth Mean Absolute Error
The Huber loss function uses a quadratic penalty (like MSE) for errors smaller than δ (delta), and a linear penalty (like MAE) for errors larger than δ.
δ is a tunable hyperparameter that defines what counts as an outlier, and sets the threshold where the loss function transitions from quadratic to linear. This makes the loss less sensitive to extreme values than MSE, and enables the Huber loss function to be effective for data prone to outliers.
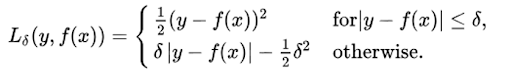
4. Log-Cosh Loss
The log-cosh loss function is defined as the logarithm of the hyperbolic cosine of the prediction error. It’s another function used in regression tasks that’s much smoother than MSE loss.
While log-cosh is smooth and somewhat robust to outliers, its behavior differs from Huber loss. Huber loss has a sharp transition between quadratic and linear penalties, whereas log-cosh changes gradually without a defined threshold.
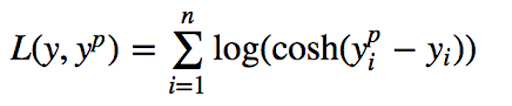
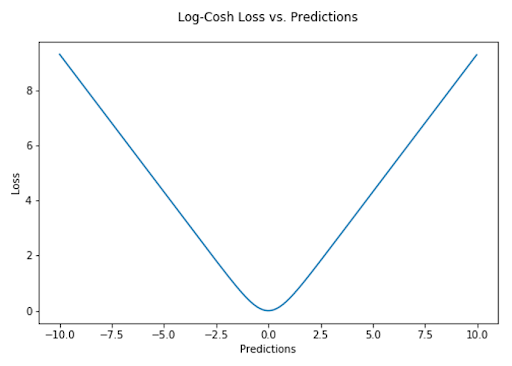
“Log(cosh(x)) is approximately equal to (x ** 2) / 2 for small x and to abs(x) - log(2) for large x. This means that ‘logcosh’ works mostly like the mean squared error, but will not be so strongly affected by the occasional wildly incorrect prediction.”
5. Quantile Loss
A quantile is a value below which a fraction of samples in a group falls. Machine learning models work by minimizing (or maximizing) an objective function. As the name suggests, we apply the quantile regression loss function to predict quantiles. For a set of predictions, the loss will be the average of the weighted absolute errors according to the chosen quantile
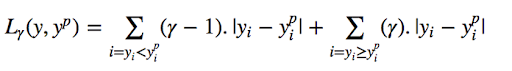
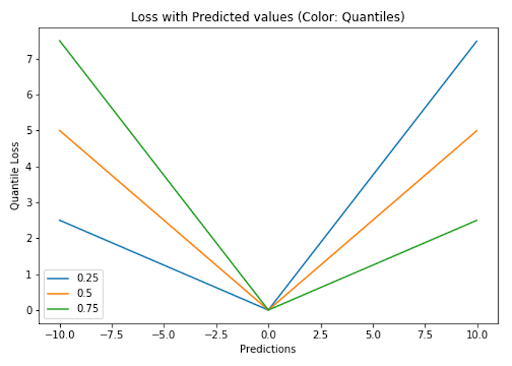
Quantile loss function turns out to be useful when we’re interested in predicting an interval instead of only point predictions.
Why Loss Functions in Machine Learning Are Important
Loss functions help gauge how a machine learning model is performing with its given data, and how well it’s able to predict an expected outcome. Many machine learning algorithms use loss functions in the optimization process during training to evaluate and improve its output accuracy. Also, by minimizing a chosen loss function during optimization, this can help determine the best model parameters needed for given data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is meant by loss function?
A loss function is a mathematical function that evaluates how well a machine learning algorithm models a featured data set. Loss functions measure the degree of error between a model’s outputs and the actual target values of the featured data set.
What is an example of a loss of function?
Mean squared error (MSE) is a common example of a loss function used in machine learning, often to evaluate regression tasks. MSE calculates the mean squared difference between actual values and predicted values. The MSE loss function increases quadratically with the difference, where as model error increases, the MSE value also increases.
What is the formula for the loss function?
The formula for the mean squared error (MSE) loss function is:
MSE = (1/n) * Σ(yᵢ - ŷᵢ)²
What is the difference between a loss function and a cost function?
A loss function measures the error for a single training sample, while a cost function is the average of all loss values across the data set. Both are used to guide model optimization during training.





