A fully connected layer (or dense layer) is a type of layer in a neural network where every input neuron is connected to every output neuron. In other words: Each neuron in a fully connected layer receives input from every neuron in the previous layer.
A convolutional layer is a neural network layer that applies filters to local regions of input data to extract spatial features like edges or textures. It uses shared weights and local connections, making it efficient for image and signal processing tasks.
What Is a Fully Connected Layer and a Convolutional Layer?
A fully connected layer is a type of neural network layer where each neuron is connected to every neuron in the previous layer, enabling global feature learning. A convolutional layer, by contrast, uses filters that connect only to local regions of the input, allowing it to detect spatial patterns like edges or textures while using fewer parameters.
Deep learning has grown rapidly in recent years, driven by advances in hardware and model architecture. Two foundational network types — fully connected neural networks (FCNNs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) — form the basis for most modern deep learning models.
Designing a neural network can be challenging at first — it requires selecting layer sizes, activation functions and where to apply techniques like batch normalization or dropout.
I’ll first explain how fully connected layers work, then convolutional layers before finally going over an example of a CNN.
What Is a Fully Connected Layer?
Neural networks are a set of dependent non-linear functions. Each individual function consists of a neuron (or a perceptron). In fully connected layers, the neuron applies a linear transformation to the input vector through a weights matrix. Each neuron applies a linear transformation followed by a non-linear activation function f.
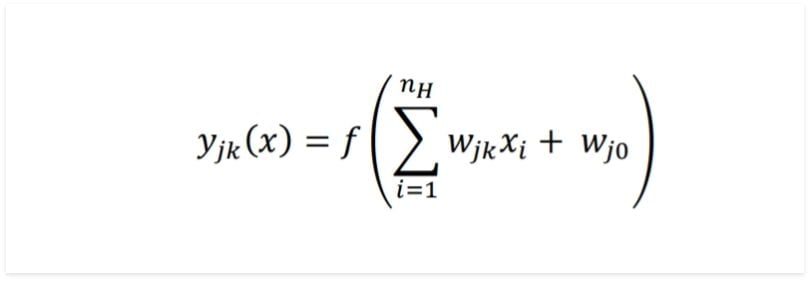
Here, we are taking the dot product between the weights matrix W and the input vector x. The bias term (W₀) can be added inside the non-linear function. I will ignore it for the rest of the article as it doesn’t affect the output sizes or decision-making and is just another weight.
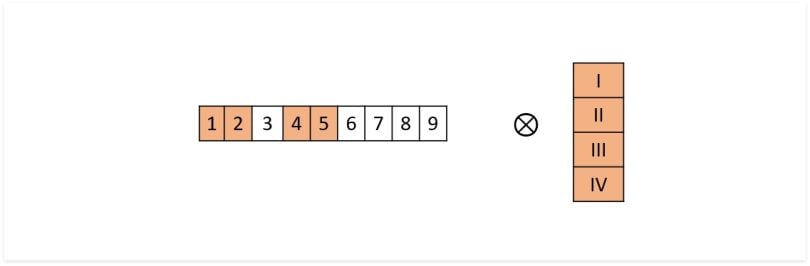
If we take a layer in a fully connected neural network with an input size of nine and an output size of four, the operation can be visualized as follows:
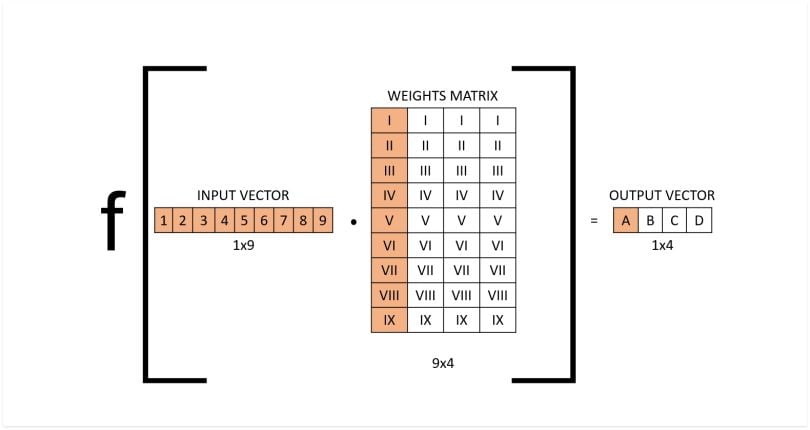
The activation function f wraps the dot product between the input of the layer and the weights matrix of that layer. Note that the columns in the weights matrix would all have different numbers and would be optimized as the model is trained.
The input is a 1x9 vector, the weights matrix is a 9x4 matrix. By taking the dot product and applying the non-linear transformation with the activation function we get the output vector (1x4).
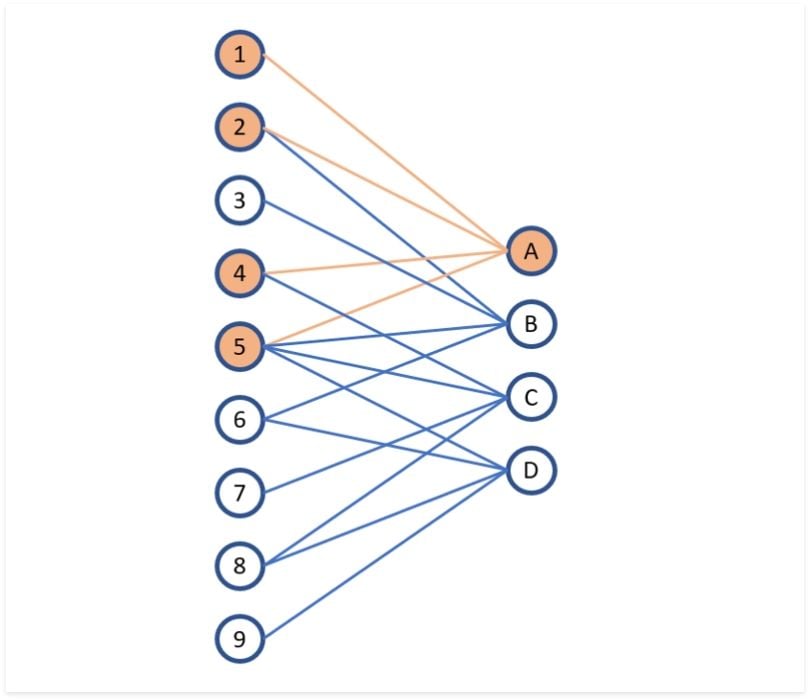
You can also visualize this layer the following way:
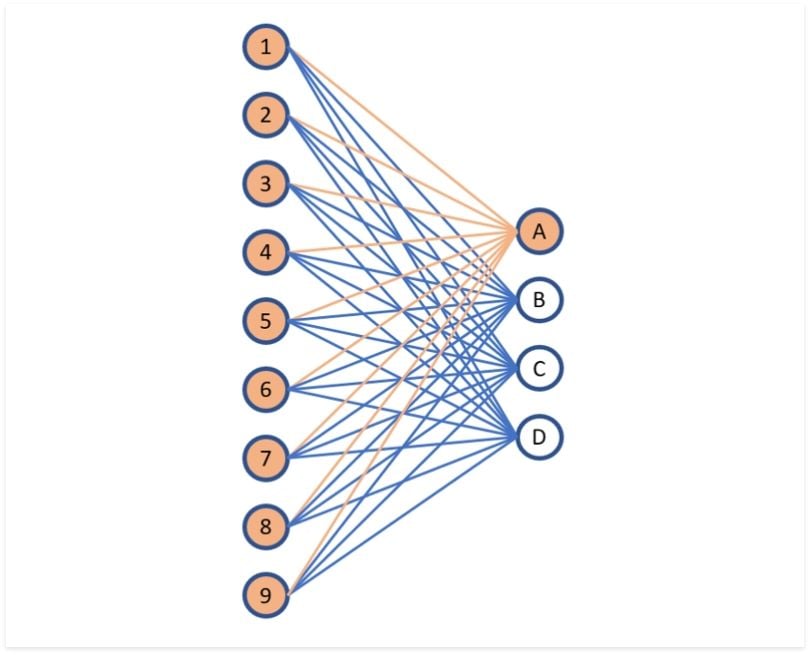
Why Is It Called a Fully Connected Layer?
The image above shows why we call these kinds of layers “fully connected” or sometimes “densely connected.” In fully connected layers, each output neuron can be influenced by the entire input vector, depending on the learned weights.
However, not all weights affect all outputs. Look at the lines between each node above. The orange lines represent the first neuron (or perceptron) of the layer. The weights of this neuron only affect output A, and do not have an effect on outputs B, C or D.
What Is a Convolutional Layer?
A convolutional layer is a neural network layer that applies convolution operations to input data. A convolution is effectively a sliding dot product, where the kernel shifts along the input matrix, and we take the dot product between the two as if they were vectors. In a convolutional layer, not all input neurons are connected to the output neurons.
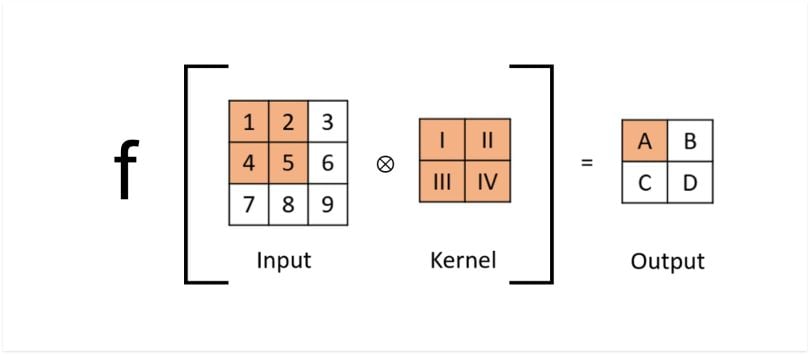
Below is the vector form of the convolution shown above. You can see why taking the dot product between the fields in orange outputs a scalar (1x4 • 4x1 = 1x1).
Once again, we can visualize this convolutional layer as follows:
Convolutions are not densely connected; not all input nodes affect all output nodes. This gives convolutional layers more flexibility in learning. Moreover, the number of weights per layer is a lot smaller, which helps with high-dimensional inputs such as image data. These advantages are what give CNNs their well-known characteristic of learning features in the data, such as shapes and textures in image data.
How to Work With Fully Connected Layers and Convolutional Neural Networks
In fully connected layers, the output size of the layer can be specified very simply by choosing the number of columns in the weights matrix. The same cannot be said for convolutional layers. Convolutions introduce several hyperparameters — like kernel size, stride and padding — that control how outputs are computed.
In this explanation of convolutions, you’ll see all the variations of convolutions, such as convolutions with and without padding, strides, transposed convolutions and more. It’s a useful visual interpretation of a convolution.
How to Calculate the Output Size of a Convolutional Layer
To determine the output size of the convolution, the following equation can be applied:
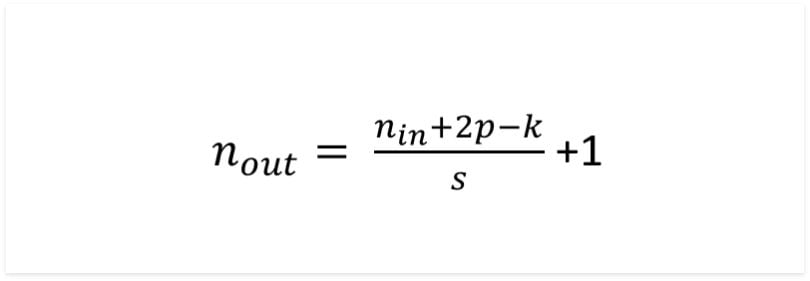
The output size is equal to the input size plus two times the padding minus the kernel size over the stride plus one. Most of the time we are dealing with square matrices, so this number will be the same for rows and columns. If the fraction does not result in an integer, we round up. It’s important to understand the equation. Dividing by the stride makes sense for the reason that when we skip over operations, we are dividing the output size by that number. Two times the padding comes from the fact that the padding is added on both sides of the matrix, and therefore is added twice.
How to Find the Transposed Convolutional Size
In standard convolutions, the output is typically smaller than the input unless padding is applied to preserve dimensions. However, padding alone can’t meaningfully expand spatial size, and adding too much padding to increase the dimensionality would result in greater difficulty in learning, as the inputs to each layer would be very sparse.
To combat this, transposed convolutions are used, which upsample feature maps and increase output resolution. Example applications can be found in convolutional variational autoencoders (VAEs) or generative adversarial networks (GANs).
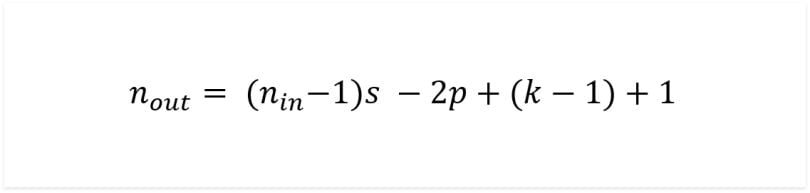
The above equation can be used to calculate the output size of a transposed convolutional layer.
With these two equations, you are now ready to design a convolutional neural network. Let’s take a look at the design of a GAN and understand it using the equations above.
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) Example With Convolutional and Transposed Convolutional Layers
As an example, I’ll use Python to go through the architecture of a GAN that uses convolutional and transposed convolutional layers. You’ll see why the equations above are so important and why you cannot design a CNN without them.
Let’s first take a look at the discriminator:

The input size to the discriminator is a 3x64x64 image, the output size is a binary 1x1 scalar. We are heavily reducing the dimensionality, therefore standard convolutional layers are ideal for this application.
Note that between each convolutional layer (denoted as Conv2d in PyTorch) the activation function is specified (in this case LeakyReLU), and batch normalization is applied.
Convolutional Layer in Discriminator
nn.Conv2d(nc, ndf, k = 4, s = 2, p = 1, bias=False)
The first convolutional layer applies the number of dimensions of the feature maps (ndf) convolutions to each of the three layers of the input. Image data often has three layers, one each for red, green and blue (RGB images). We can apply multiple convolution filters to increase the number of output feature maps — sometimes referred to as the depth or channel dimension of the data.
The first convolution applied has a kernel size of four, a stride of two and a padding of one. Plugging this into the equation gives:
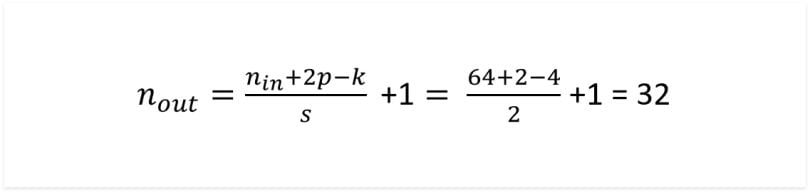
So the output is a 32x32 image, as is mentioned in the code. You can see we have halved the size of the input. The next three layers are identical, meaning the output sizes of each layer are 16x16, then 8x8, then 4x4. The final layer uses a kernel size of four, stride of one and padding of zero. Plugging into the formula we get an output size of 1x1.
Transposed Convolutional Layer in Generator
nn.ConvTranspose2d( nz, ngf * 8, 4, 1, 0, bias=False)

Let’s look at the first layer in the generator. The generator has an input of a 1x1x100 vector (1 x nz), and the wanted output is a 3x64x64. We are increasing the dimensionality, so we want to use transposed convolution.
The first convolution uses a kernel size of four, a stride of one and a padding of zero. Let’s plug it in the transposed convolution equation:
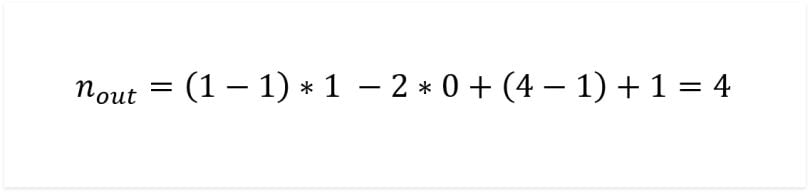
The output size of the transposed convolution is 4x4, as indicated in the code. The next four convolutional layers are identical with a kernel size of four, a stride of two and a padding of one. This doubles the size of each input. So 4x4 turns to 8x8, then 16x16, 32x32 and finally, 64x64.
Understanding these fundamentals is essential for designing effective CNNs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a fully convolutional network?
A fully convolutional network (FCN) is a type of neural network architecture that uses only convolutional layers, without any fully connected layers. FCNs are typically used for semantic segmentation, where each pixel in an image is assigned a class label to identify objects or regions.
What is the difference between CNN and FCN?
CNNs (convolutional neural networks) typically combine convolutional and fully connected layers and are used for tasks like image classification or object detection. FCNs (fully convolutional networks), by contrast, remove fully connected layers entirely and output segmentation maps that retain the spatial dimensions of the input, making them suitable for pixel-level tasks like semantic segmentation.





