Thanks to the rise of generative AI tools, we can now create a flurry of images with just a few words and clicks.
What Is AI Art?
AI art is any kind of image, text, video, audio or other kind of digital artwork produced by generative AI tools. These tools are fed millions of written, visual or aural samples of content that they can reference when creating AI-generated art.
With AI text-to-image generators, the user inputs a prompt, and the AI visualizes it. For instance, this image used the prompt: Cat bunny.
The popularity of AI art generators like Midjourney and DALL-E may have more people wondering: How does AI art work? What goes into the technical and creative choices behind each creation? And what does this mean for creatives moving forward?
What Is AI Art?
AI art is any type of digital art created by entering prompts into an AI art generator, which employs large language models trained on millions of data points. These models reference this data to process a request and produce the desired result. AI art generators can then take written or visual prompts and craft new text, images or audio clips for marketing materials, music videos and professional websites, among other mediums.
How Does AI Image Generating Work?
While the visual distinction between a sandwich and a pineapple may be clear to you, it’s a trickier task for a computer. Researchers must feed machines millions upon millions of images. They annotate the data sets, so the machine has a text reference, and the device is tweaked and calibrated until it can recognize the photos. Thus, it begins to parse pineapples from sandwiches and can start to make its own.
These new tools are mind-boggling. And public. On September 28, 2022, OpenAI made a staggering announcement: DALLE-2 would be open and accessible to all, paving the way for a range of AI art generators to become available for public use.
The year 2022 alone saw the rise of DALL-E 2, Midjourney, Craiyon and the often controversial Stable Diffusion. If you’re looking for a bit of experimentation, these programs have free trials. Once you run out, you’ll have to subscribe to Midjourney or buy into DALL-E’s token system.
How to Use Midjourney
Midjourney’s image generator runs through the ever-popular Discord. Once you join the official server, you’ll have to navigate to Midjourney’s newbie server.
From here, the process is as simple as typing, with imagination to boot. Type “/imagine” in the chat bar and enter your prompt — this cue tells the server you’re looking for an image. For our purposes, let’s try: “Homer Simpson in an arcade.”
“/imagine Homer Simpson in an arcade.”
As soon as you hit enter, Midjourney begins to generate. Unlike other AI generators, you watch Midjourney develop in real time, likely around 30 seconds.

On the first go, the results can be confusing. Midjourney gives you a grid of images with several commands beneath it. U means “upscale,” and V means “Variation.” The number corresponds clockwise. The top left is U1, and the bottom right is U4.
If you like an image and want to see it in HD, you can choose the corresponding U to add an increased definition. If you like the idea of an image, but want to see what else it can do, click the corresponding V. Midjourney will create four different images with the same baseline.
Clicking V4 presents me with four new options:
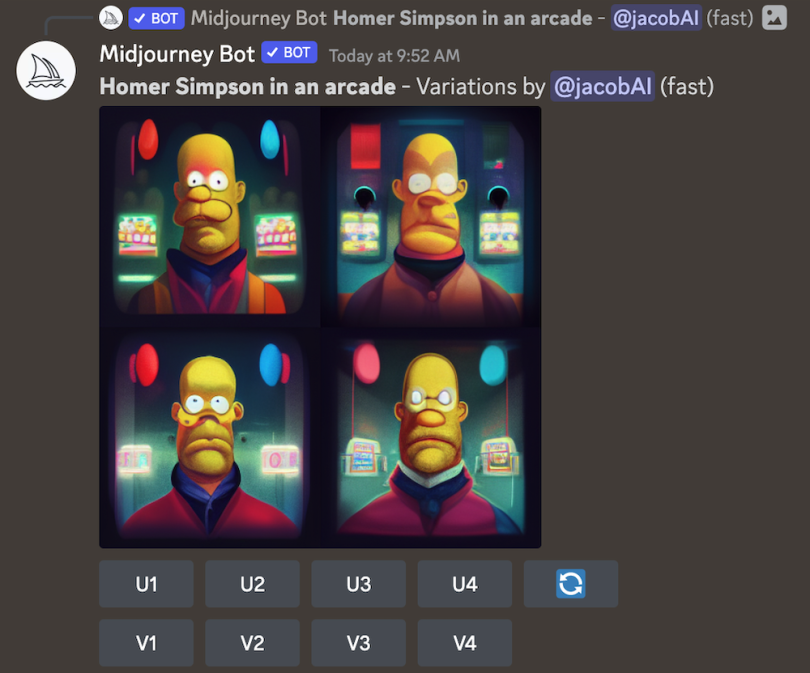
Midjourney’s generations are not as lifelike as DALL-E’s. While you can tailor the input with specific words, for instance “photorealistic,” “35mm” or “HDR,” I’ve found Midjourney much better suited for art.
If I like the top left, I select “U1” to upscale.
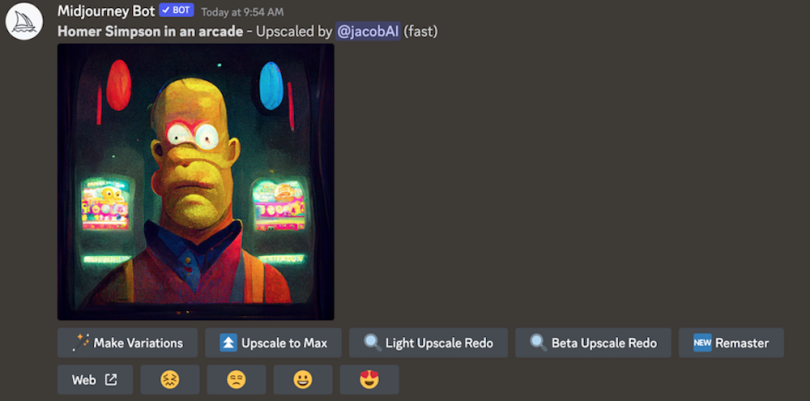
Again, I can make variations. However, if I like the image, I can “Upscale to Max” to make it as HD as possible. This is the final, high-quality result:
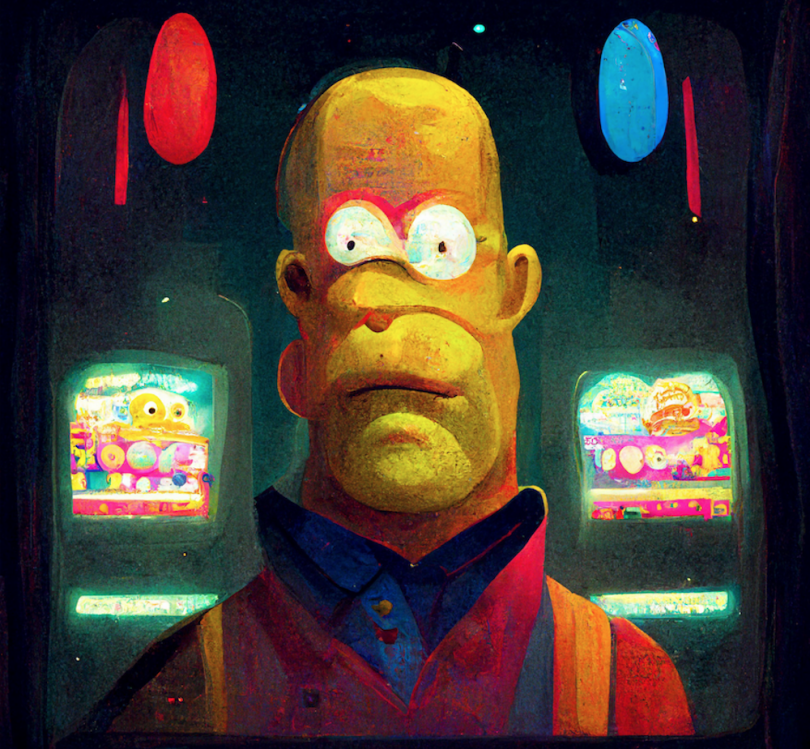

Don’t be discouraged by Midjourney’s less-than-photorealistic results. While this program may not be as poised for visual trickery, it generates lovely, intriguing artwork.
How to Use DALL-E
DALL-E is the program you boot up with your friends on Friday night to show them what AI can do. The results are often less cerebral and artistic and more outright fun.
The process itself is quite simple. You’ll arrive at the image-generation bar when you create an account for Open AI. From there, all you have to do is type. If you can’t think of anything, click ‘Surprise Me.’
Let’s try our old prompt: “Homer Simpson in an arcade.” Rather than watching the images form, you’ll track a loading bar, with some reference images below. Within 30 seconds, you’ll have your output.
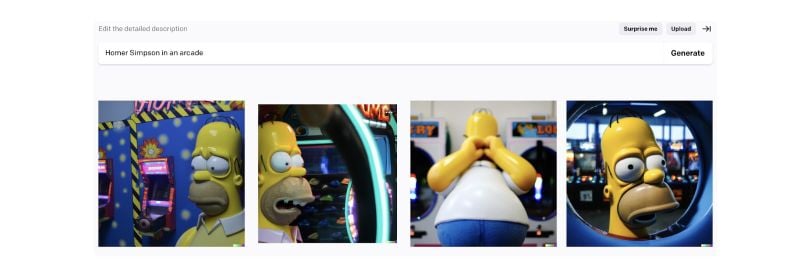
The results are typically shocking. You may wonder: What else can it do? By inputting the same prompt, you can see the limitless possibilities.
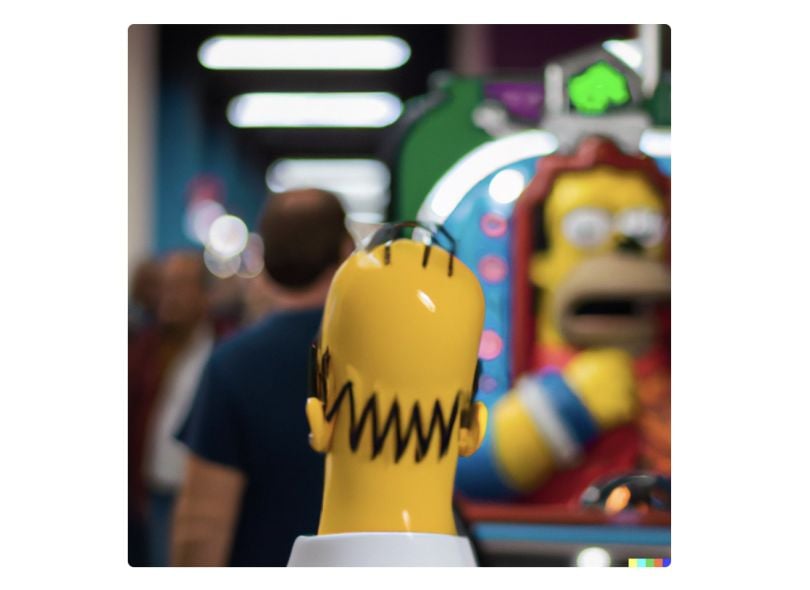

The words will often be jumbled, the figures demented, but it’s a small price to pay for images of this quality.
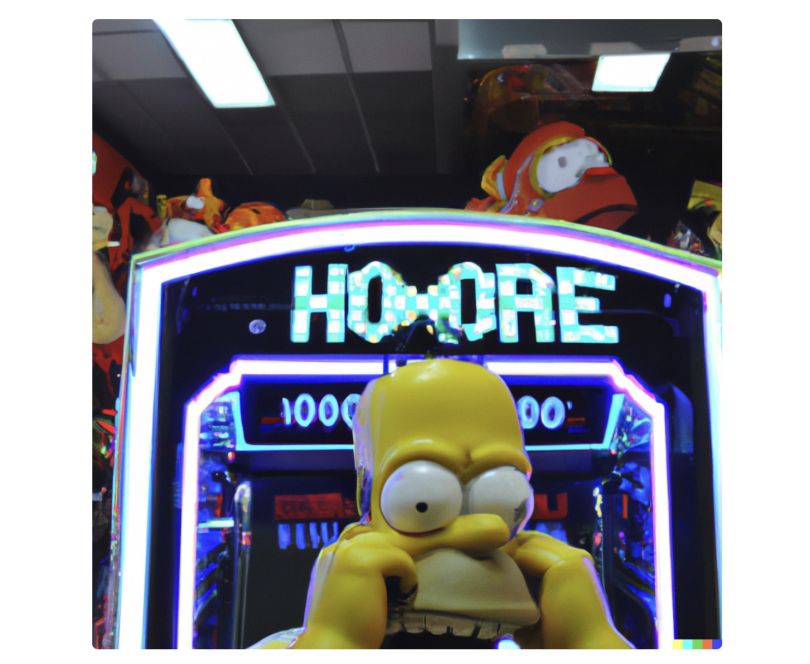

It’s important to note that DALL-E does much better with characters than humans. The program recognizes pop culture icons better and seemingly struggles to create lifelike figures with clear faces. For instance, the prompt: “A fifty-year-old plays double dutch.”

Disturbing, I know.
How to Use Stable Diffusion
Stable Diffusion is another simple process — with a twist. Your prompt is what you want to see in the image, while your negative prompt is what you don’t want to see. If I want a seedy night image, I’ll try “Daylight” as a negative prompt. The loading screen creates output in a similar time frame.
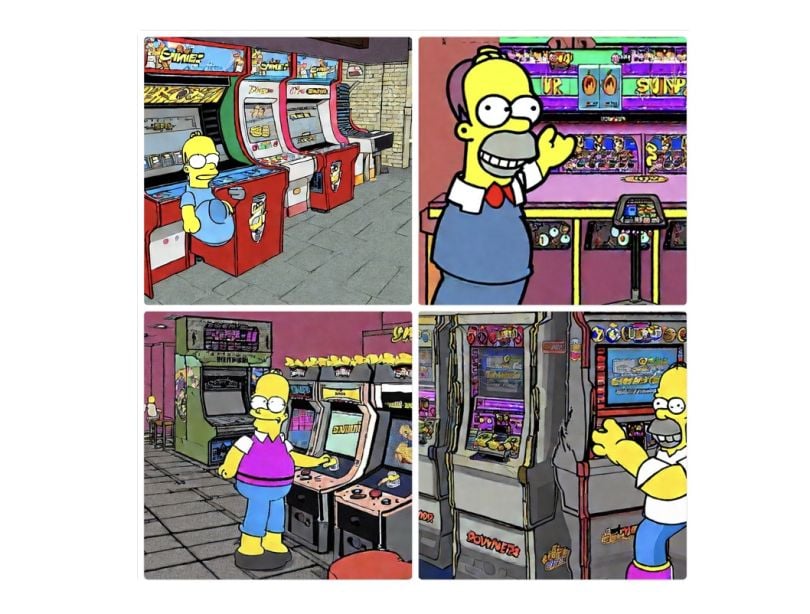

Ugly, right? This is where the negative space comes in. Below the generation stage, you can filter through Diffusion’s successful example prompts.
In the following example prompt, they wrote: “A small cabin on top of a snowy mountain in the style of Disney, artstation” with the negative prompt: “low quality, ugly.”
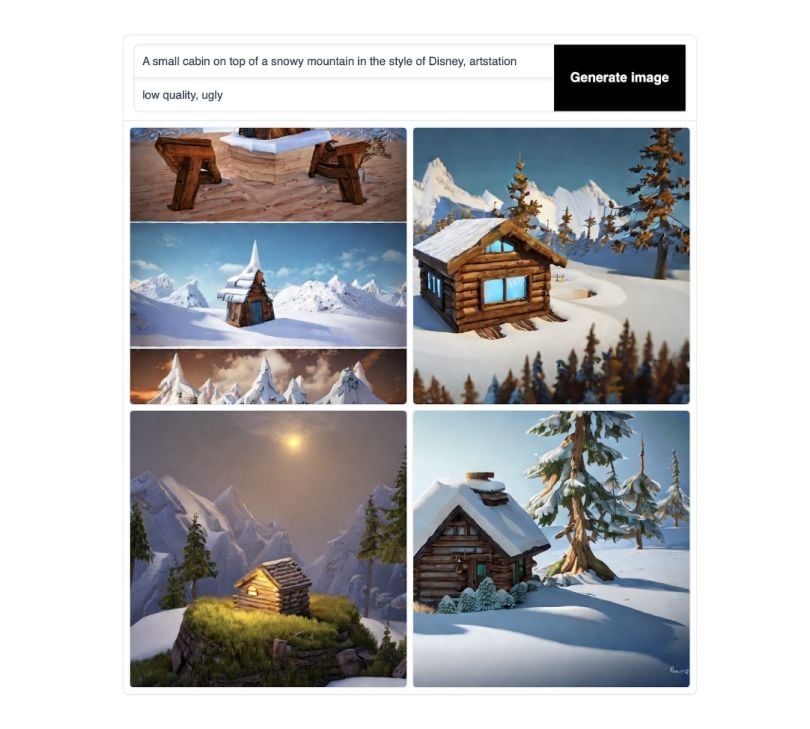
By telling Stable not to be low quality or ugly, the program created a neat, beautiful image. Let’s try the same negative prompt on ours.
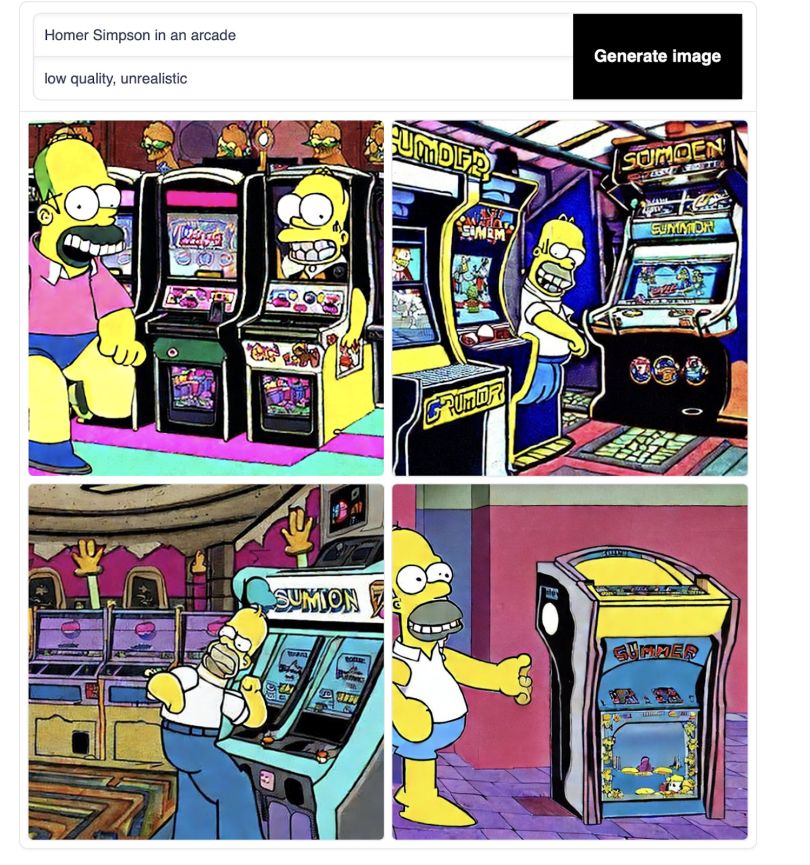
A bit better, but still not great. Let’s try to get out of the animated realm.
In the negative space, I inputted: “animated” “hand-drawn” “unrealistic” “cartoon.” Ideally, we can eliminate the ugly, early 2000s Cartoon Network look. I’d like a bit more artistry to it, like the Midjourney or DALL-E results.
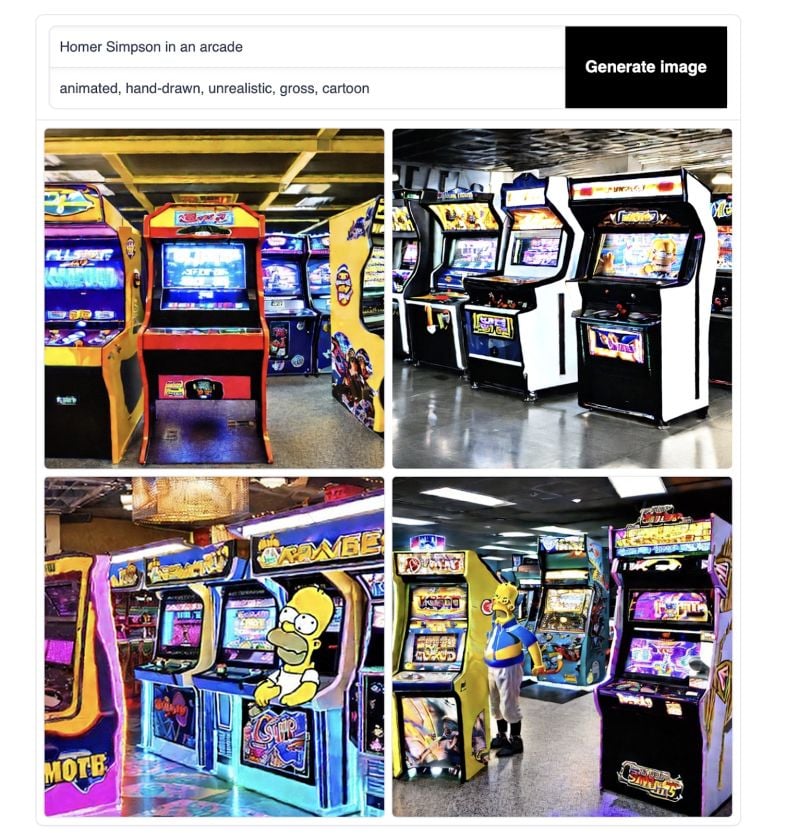
A bit better. Like Midjourney and Dall-E, you’ll have to learn the program’s language. No matter which software you choose, their communities offer a vast wealth of knowledge and tips.
Analyzing the Results
Clearly, the AI isn’t shooting baskets every time. The generations took me more than an hour, and I still may not have the images I want. While the prompting can become more specific and coded (guided toward lens sizes and aspect ratios) and each program has a community of users willing to help, there are natural limitations.
As a whole, the images could not exist without human direction. The human must have the vision, the idea and the taste to know what works and what doesn’t. In this way, the tool is still a tool, and the human is still the shaper.
AI-Generated Art: An Explosion of Creativity
It’s difficult to deny the artistry of what AI is doing. AI is pulling on a reservoir of great artists and iconic works, referencing them as an artist does, but maddeningly all at once. The ethics are unknown: copyrights questionable, accuracy tainted.
Now, anyone can create AI art images. While this opens the Internet to funny content, the AI art world is changing so fast we have little time to distinguish its possibilities from its consequences.
In 2022, a machine-generated painting titled Work theatre d’ opera spatial won the Colorado State Fair Art Show, prompting controversy in the greater art world. Its creator, Jason M. Allen, saw no issue. Already, the distinction between human and AI art is blurring. In 2018, artist Edward Bellamy auctioned AI art to a museum for $432,000.
And the train shows no signs of stopping. We are watching the future take shape in real time, image by image. If the recent upswing in AI art is anything to go by, the future will be a succession of ever-sharpening, ever-more-realistic images.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI art?
AI art is any digital artwork produced by generative AI tools. It works by a user feeding a prompt into an AI art generator, which processes the request and delivers the desired text, image, audio or other output. These generators are a form of generative AI and use large language models trained on millions of data points to understand different prompts.
How is AI able to create art?
AI art generators rely on neural networks, which are algorithms that identify patterns in data sets. As generators are fed information, neural networks learn to discern patterns and distinguish different objects from one another. An AI art generator can then respond to a prompt, recalling what a specific object looks like to generate an accurate image.
Where do AI art generators get their images?
AI art generators feature language models that have been trained on millions of samples of text, images, audio clips and other digital media. While some of this information is found in publicly available data sets, data scraped from across the web is also used to train models. This practice has sparked debate about whether AI art generators are trained on copyrighted material, leading to legal battles between AI companies and artists.
Do you own the AI art you create?
According to the U.S. Copyright Office, a work can only be copyrighted if a human creator is involved. Because AI-generated pieces aren’t considered to be the work of humans, they can’t be copyrighted or owned.
Is AI-generated art really art?
AI-generated art may mimic previous works and styles of humans, but AI artworks are not original pieces. Many also believe AI art generators are just another tool, so whoever uses the tool to create a digital work can be considered the artist of the AI-generated piece. Still, whether AI-generated art is really art remains up for debate.





