In process mining, we use algorithms to analyze event data and reveal details about the activities performed by people and machines.
Process mining has a wide range of applications across various disciplines including finance, healthcare, manufacturing and logistics. It’s an interdisciplinary field that combines techniques from data mining, machine learning and process management to discover, monitor and optimize real-world business processes. With process mining, organizations can increase efficiency and ensure widespread compliance.
Process Mining Definition
Process mining involves taking log data from different enterprise systems and analyzing it to understand how to improve various processes. With process mining tools, teams can transform data into visualizations to locate bottlenecks and adjust workflows accordingly.
How Does Process Mining Work?
In a typical process mining scenario, we collect data from various sources such as an organization’s transaction logs, ticketing systems, ordering systems, and CRM (customer relationship management) and ERP (enterprise resource planning) systems in the form of event logs.
You can see a simple event log from a hospital below. To properly develop the process model, event logs should contain case ID, activity and timestamp information at the minimum.
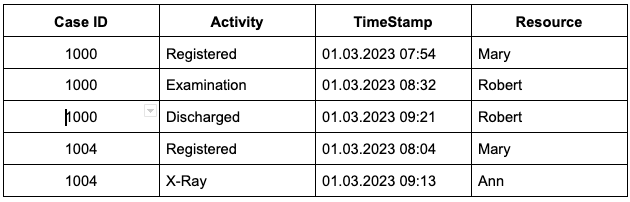
Here, case ID represents a specific instance of the process from start to finish. A case ID can have many activities with different timestamps. In the table above, case ID of 1000 covers a specific service provided to a patient, which contains three different activities.
Timestamps provide critical records of when the activities occurred and in what order. Process mining algorithms use this information to generate process flows, measure performance and monitor compliance.
Process mining algorithms scan the event logs to provide insight into the structure of the underlying process. We then process the outcome of the analysis using specialized software tools that can visualize the process flow, identify inefficiencies and detect patterns.
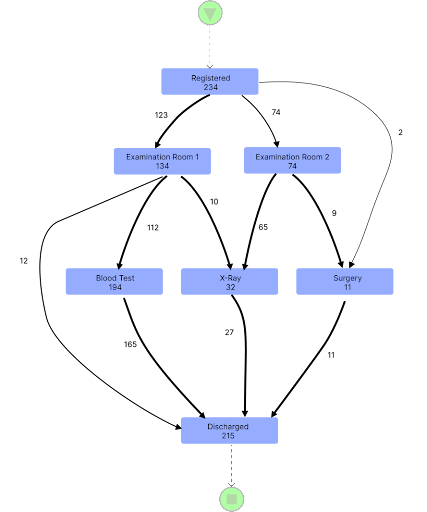
Frequency Counts
The process map above displays the daily frequency of activities. In a single day, examination room one handled 134 patients and examination room two covered 74 patients.
Cycle Times
The process map uses timestamps to display the cycle times for a particular task from start to finish while also providing information about the average cycle times over weeks and months.
Resource Utilization
When management analyzes the process map above, they can see 194 patients (83 percent of registered patients) received blood tests while only 32 X-ray tests were conducted on this day. This data helps management allocate resources based on the demand for different tests.
Process Variants and Deviations
Process maps can show process variants including deviations from the expected process flow. This helps identify areas of the process that need to be standardized or optimized. In the process map above, you can see that although 234 patients are registered, 215 of them are discharged by the hospital. That means 19 patients left the hospital without being examined and discharged. Once we investigate, we may find that patients are leaving the hospital without being seen due to the long wait times.
Types of Process Mining
3 Types of Process Mining
- Discovery
- Conformance
- Enhancement
1. Discovery
In some cases, an organization may not have a proper process model definition. In such cases, we would use process mining to develop a process model.
Alpha-algorithm, heuristic-mining algorithm and genetic-process-mining algorithm are among the algorithms we use to extract process models from the event logs. Process discovery algorithms scan through all the events in the log to develop the process model.
We can then develop graphical representations of the process models using industry-standard notations such as directly-follows graphs, petri-nets, and BPMN 2.0 (Business Process Model and Notation).
2. Conformance
Organizations often have an ideal process model in place that defines how a process is supposed to work. In conformance process mining, the actual execution of a process is compared with a predefined process model. Conformance-type process mining aims to identify deviations that may include redundant or unnecessary steps, as well as missed or incorrectly sequenced steps.
This information can help organizations identify inefficiencies, non-compliance with regulations or standards and other areas for improvement.
3. Enhancement
Once we develop the process model and identify the areas for improvement, process mining enhancement involves redesigning the process to optimize its efficiency and effectiveness. This process includes eliminating unnecessary steps, automating repetitive tasks and reallocating resources, all while improving team communication and collaboration.
Why Is Process Mining Important?
Company leaders and executives may think they know the ins and outs of a business, but lack the data to back up their claims. Process mining removes any guesswork and false assumptions by translating log data into visual models and representations. With a more accurate view of daily operations, leaders can understand what’s truly working for the company and what processes need adjusting.
Teams can use these insights to reallocate resources and better apply employees’ time and energy. By making these adjustments, company leaders can raise teams’ performance, improve the customer experience, cut down on unnecessary costs and boost revenue streams.
Benefits of Process Mining
Process Flow, Variations and Exceptions
The process model clearly shows the process steps and their sequences as well as process variations and exceptions (if there are any). With this information, you can identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks and opportunities for operational improvement.
Process Performance Metrics and Resource Utilization
Process mining helps you see the process performance metrics and resource utilization more clearly. This means you can get a better idea of how organizations use resources including people, machines and materials. This information helps organizations optimize resource allocation and improve overall efficiency.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Process models demonstrate deviations from compliance and regulatory requirements. Organizations use this information to ensure that the process is aligned with legal and regulatory standards.
Tools for Process Mining
Celonis
Celonis offers execution management solutions to help organizations optimize their business processes. They provide a suite of process mining capabilities that allow companies to gain better visibility into their operations, identify areas of inefficiency and streamline their workflows. These capabilities leverage machine learning, industry-standard process query language (PQL) and include features such as:
- Customizable analytic visualizations
- Task mining
- Flexible data models
- Support for multiple event logs
- Benchmarking against industry best practices
- Identification of processes ripe for automation
Fluxicon Disco
Fluxicon is a provider of process mining solutions designed for business process managers and consultants. The company’s flagship product, Disco, offers a range of advanced features, including process map animations, detailed statistics, interactive charts, automated process discovery and user-friendly log filters that allow users to drill deeper into their data. Additionally, Disco provides project management capabilities and performance filters while supporting various data import and export options.
IBM Process Mining
IBM’s suite of process mining products leverages data-driven insights to enable companies across various industries to enhance their processes and make informed decisions quickly. IBM’s process mining solutions have numerous use cases, such as intelligent automation, customer onboarding, P2P (procure to pay), accounts payable, IT incident management and order-to-cash.
IBM’s process mining tools offer features such as automated RPA (robotic process automation) generation, fact-based process models, AI-driven process simulations, conformance checking, task mining and seamless integrations with leading software providers like SAP, Oracle and other IBM products.
Process Mining Use Cases
Customer Service
Through CRMs, companies can use process mining to compile data from customer tickets. Leaders can then observe common questions and complaints to determine what pain points and challenges exist within a product or service and how they can be resolved.
Sales
Companies can assess the sales cycle, evaluating the length of time to convert prospects and how larger market trends impact their sales teams. With process mining, leaders can then uncover roadblocks in the sales funnel, adjusting teams’ goals accordingly and finding ways to shorten the sales cycle while increasing conversions.
Logistics
Process mining allows businesses to take a deeper look at their warehouses and inventories. Teams can keep better track of inventory, ensuring warehouses are neither under- nor overfilled. Companies can also assess processes, uncovering inefficiencies and readjusting workflows to help warehouse and logistics teams run more smoothly.
Manufacturing
Organizations can rely on process mining to review workflows and determine which tasks they can automate to speed up production. For companies that have adopted machines like robotic arms, teams can use process mining to gather data on how long machines last and inform their predictive maintenance practices.
Finance
Process mining can be a major boon for companies looking to straighten out their finances. Since maverick buying is a nuisance to many businesses, leaders can apply process mining to audits and root out any unusual spending behavior among employees.
Insurance
Assessing risk can be a challenge in the insurance industry, but process mining can simplify this task. By analyzing a company’s historical data, process mining allows teams to understand red flags during the underwriting process that hint at more risk. This way, underwriters can more accurately assess risk and avoid greater expenses later on.
E-Commerce
E-commerce companies can employ process mining to track customers’ behavior across different web pages. With a better idea of what journey customers take to purchase a product online, teams can better organize web pages, remove technical hiccups and fix any other inefficiencies to improve customers’ experiences and increase purchases.
IT
IT teams can use process mining to more closely evaluate their IT environments. Based on their findings, IT personnel may decide to buy new technologies, update old systems and automate workflows to improve their company’s tech stack.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry is often plagued with slower workflows, which process mining is designed to eliminate. Healthcare groups can take data from patient visits and enterprise systems to see what daily activities take too long and can be automated. This way, patients can enjoy shorter wait times and more quickly receive the treatment they need.
Education
Tapping into daily student logs, schools can monitor variables like students’ attendance and grades to proactively address the behavior of at-risk students. Schools using online learning platforms can also track factors like course content and video length to understand why students spend more or less time on assignments.
Process Mining Best Practices
Process mining can deliver positive results for a business when done right. To increase the chances of success, leaders can follow these best practices for process mining.
- Establish goals: Businesses need to know why they’re embracing process mining in the first place. With a clear set of goals, teams can understand how to best apply process mining to achieve outcomes most helpful to the company.
- Involve different teams: Process mining affects every aspect of an organization. By involving various teams, leaders can understand how new workflows and technologies could impact different departments and plan accordingly.
- Pick the right tools: There are plenty of process mining tools on the market. Companies most successful at adopting process mining pick platforms that align with their goals, needs and preferences.
- Maintain transparency: Process mining may involve reorganizing many elements of an organization. By constantly communicating changes, leaders can adjust workflows and reallocate resources without causing confusion.
- Assess results: Change in itself isn’t necessarily a good thing. To make sure process mining is delivering the intended results, company leaders can evaluate factors like operational costs and productivity levels for signs of improvement.
- Gauge customer satisfaction: Another good way to measure the success of process mining efforts is to analyze the customer experience. Customers are more likely to be satisfied with higher-quality products, less pain points and faster workflows.
- Integrate into your business: To enjoy the long-term effects of process mining, businesses can make this method a part of their core operations. Constantly seeking ways to optimize workflows ensures companies keep performing at peak levels.
Process Mining vs. Data Mining
Process mining and data mining are both fields that involve the analysis of large data sets, but they have distinct differences.
- Process mining focuses on analyzing and improving business processes while data mining focuses on discovering patterns and insights in data sets more generally.
- Process mining mainly uses event logs or transaction data generated by business processes, whereas data mining uses a variety of data sources, including social media, customer and financial data.
- Process mining techniques are specifically designed to analyze the behavior of business processes, such as process discovery, conformance checking and performance analysis. Data mining techniques, on the other hand, are more general and can include clustering, classification and regression.
Process mining objectives are primarily aimed at improving the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes. In contrast, data mining can have a wider range of goals, such as identifying new marketing opportunities, detecting fraudulent activities or predicting customer behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does process mining work?
Process mining compiles log data from enterprise systems and uses algorithms to analyze the data and reveal trends. With these insights, companies can reallocate resources, adopt new technologies and perform other actions to simplify workflows, improve employee performance and generate more revenue.
What are the three categories of process mining techniques?
The three categories of process mining techniques are discovery, conformance and enhancement.
What is process mining used for?
Process mining is used to visualize, monitor and improve business processes by analyzing event log data from systems like CRM and ERP.
Which industries use process mining?
Industries such as healthcare, finance, logistics, manufacturing, insurance, e-commerce, IT and education use process mining to improve performance.
How is process mining different from data mining?
Process mining focuses on analyzing business processes using event logs, while data mining looks for patterns in broader data types for various goals.