These days, four out of every five U.S. organizations use low-code or no-code solutions for business automation and app development, and the global low-code development market is expected to reach $50 billion by 2028. While this has sparked concerns over automation tools replacing human developers, many experts argue that no-code and low-code platforms will breed a newer, better class of developers, bridging the gap between IT and business operations teams.
What Are Low-Code Platforms?
Low-code platforms enable developers to write code using a graphical user interface that contains visual models and drag-and-drop features. Because these platforms require less manual coding and automate parts of the development process, even non-technical developers can quickly write code for applications and other products.
No-code tools require zero coding, are entirely visual and are designed primarily to give citizen developers the ability to create apps without help from professional developers. Low-code platforms run on drag-and-drop elements, and leave room for small bits of code to allow for customization and other supplementation. With low code, it’s all about eliminating the grunt work for developers and allowing them to handle more complex tasks.
Big names like Microsoft and Apple offer their own low-code solutions, and countless companies have been cropping up over the years to claim a piece of this increasingly lucrative pie. To learn about some of the most useful tools on the market today, check out these 22 low-code development platforms.
Top Low-Code Platforms
- Airtable
- Webflow
- Wordpress
- Oracle APEX
- Google AppSheet
- Microsoft Power Apps
- Contentful
- UiPath
Low-Code Platforms to Know
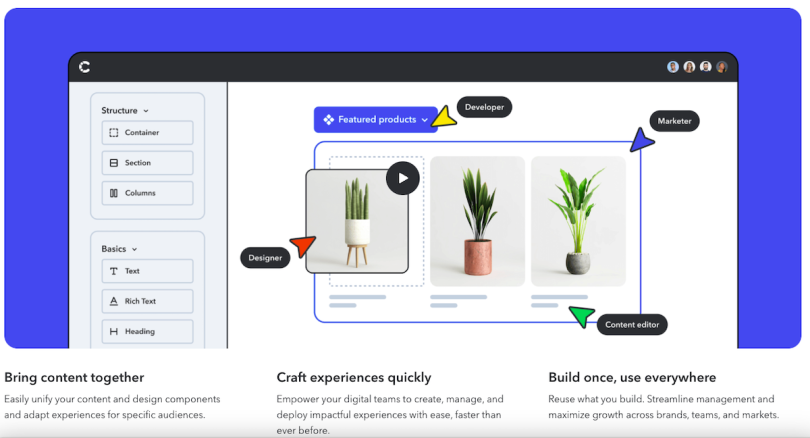
Contentful
Contentful offers a composable content platform with AI capabilities designed to simplify content creation and distribution processes. Its products are intended for both technical and non-technical users alike. By leveraging advanced AI tools, businesses can accelerate their publishing timelines, extend market presence and elevate customer engagement levels. Contentful’s platform supports a wide range of industries.
Contentful Top Uses:
- Automatically distribute content across web and mobile channels.
- Create custom browsing experiences for users and shoppers based on their demographic data.
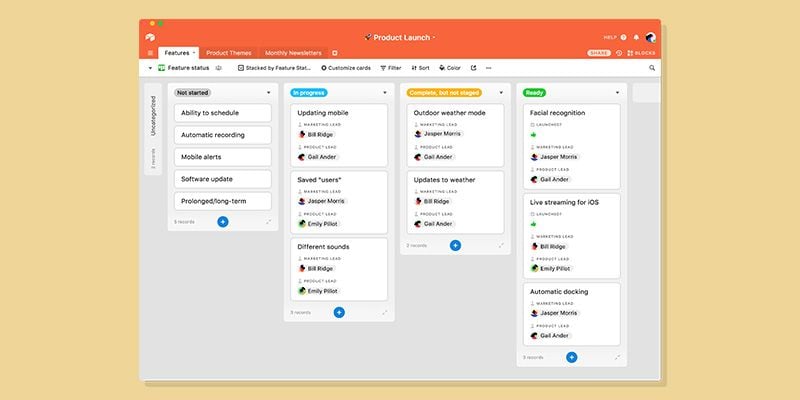
Airtable
Perhaps the most familiar name on this list, Airtable has been at the forefront of the low-code movement for about a decade, allowing users to build complex spreadsheets and workflows with little to no code on the back end. It also launched a new Interface Designer tool in 2021, which helps teams design fully interactive, front-end experiences and apps.
Airtable Top Uses:
- Build custom operational dashboards with project management features and automations.
- Create hybrid databases that link spreadsheets and traditional relational databases.
Anima
Anima aims to help developers code faster by automating what it calls the “design-to-code process,” sparing them the grunt work that comes with coding a product’s user interface from scratch. This can be applied to doing everything from building prototypes to creating interactive elements like buttons and animations. And to ensure that the quality of the code it generates remains high, Anima says it regularly updates and optimizes its AI, paying special attention to React code.
Anima Top Uses:
- Transform Figma projects into React, HTML, Vue and Tailwind CSS components.
- Convert Adobe XD UI and visual elements into code.
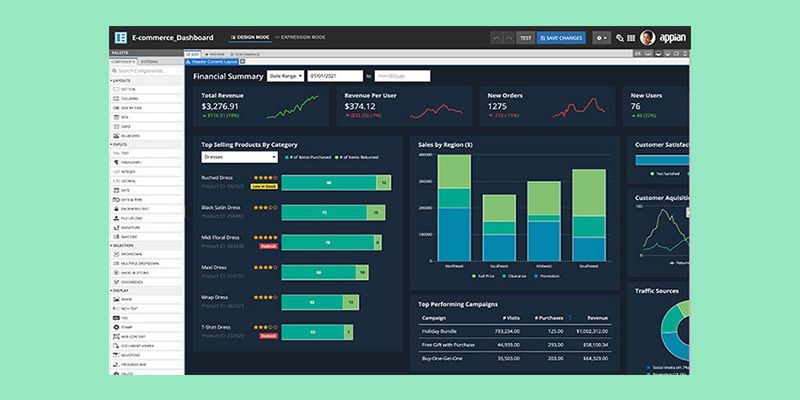
Appian
Companies like Bayer, Ryder and T-Mobile use Appian to organize their data, build new apps, enhance their existing ones and automate whatever repetitive tasks they have. The company claims it can help develop and deploy mobile-native apps 10 times faster than those built without its low-code platform, all in a single workflow.
Appian Top Uses:
- Build web and mobile applications using a visual design platform.
-
Create autonomous AI agents with highly specific workflows and escalation paths.
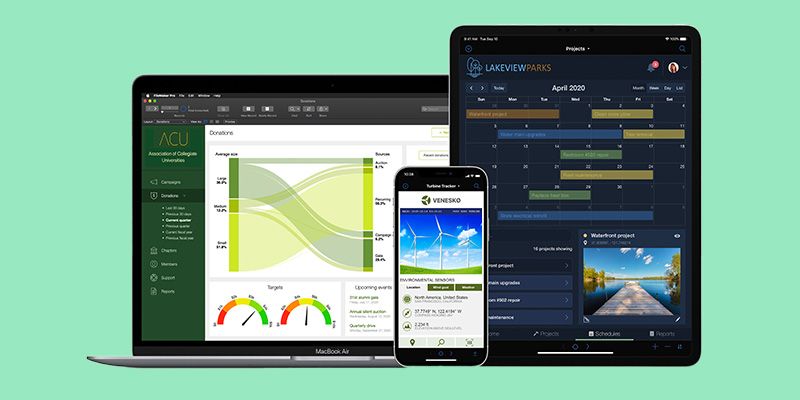
Claris
After operating under the name FileMaker for more than two decades, the Apple-owned software company returned to its original name from the 1980s, Claris, in 2019. With built-in templates, drag-and-drop design and an intuitive UI, Claris allows businesses to build any app they want and deploy it for any device on that same day. They can also easily add things like calendars, kanban boards and photo galleries with no advanced coding experience required.
Claris Top Uses:
- Build custom applications with a drag-and-drop interface.
- Easily deploy productivity tools such as kanban boards and project management dashboards.
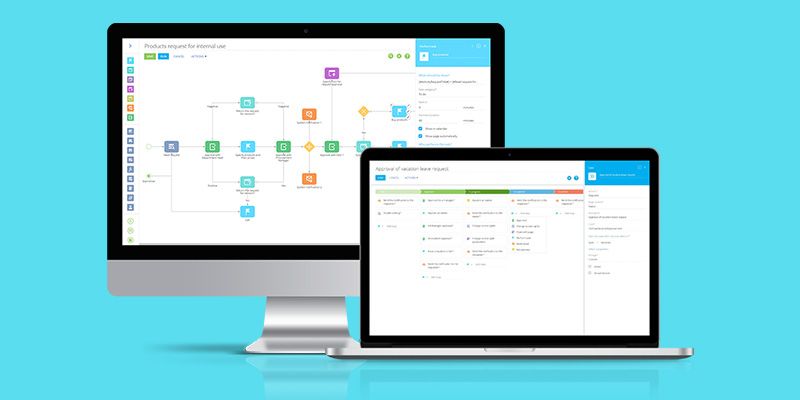
Creatio
Creatio helps mid-size and large companies automate their customer-facing operations, with a specific focus on industries related to financial services and manufacturing. Its low-code platform for process management and customer relationship management is designed to let users customize their products quickly and accelerate their sales without having to wade through complex code.
Creatio Top Uses:
- Drive sales initiatives with AI-enabled features for clients.
- Automate analytics and generate sales summaries using internal data.
Heroku
As a business unit of Salesforce, Heroku allows companies to leverage the customer data they house in Salesforce to build apps that span both platforms. It is a container-based cloud platform as a service, or PaaS, which means it lets users deploy, manage and scale their apps with very little code or grunt work. But, for the times users do have to code, Heroku embraces common languages like Ruby, Java and Python, allowing developers to code comfortably and quickly.
Heroku Top Uses:
- Deploy applications in smart containers optimized for scalability.
- Ensure continuous protection of data and PostgreSQL databases.
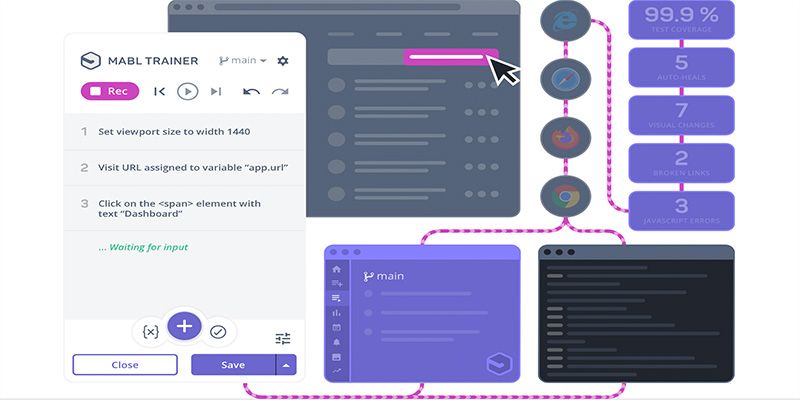
Mabl
The recent acceleration of low-code tools means apps have been able to get developed faster than ever before, but the tech required to actually maintain and secure these apps hasn’t quite caught up with the times. That’s where Mabl comes in. Pulling content from internal sources like emails and PDFs, the platform makes it easy for companies to create and run automated UI tests at scale, as well as keep tabs on how well a given test covers an app. Mabl is used by several leading companies, including Chewy and Dollar Shave Club.
Mabl Top Uses:
- Leverage AI for QA processes and automated website testing.
- Create browser and API load tests to monitor app and network performance.

Mendix
Mendix helps companies develop and deploy their own customer portals, mobile apps and accounting tools. The company was acquired by industrial manufacturing giant Siemens back in 2018, and has been combined with its IoT platform MindSphere to tap into the massive amounts of data smart devices collect and turn them into real-time business value.
Medix Top Uses:
- Build custom user portals and mobile applications.
- Aggregate IoT device data and discover insights for further development or business decisions.
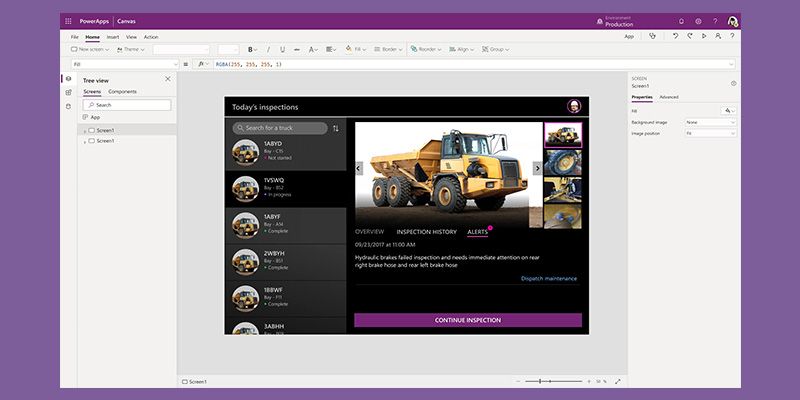
Microsoft Power Apps
Microsoft is synonymous with innovation in many tech spheres — quantum computing, mobile gaming and cloud computing, to name a few. It’s also a player in the low-code development game. Its platform Power Apps is capable of instantly generating web and mobile apps directly from design files and images like paper forms, PDFs, sketches and even professionally designed assets in Figma. It also includes features like cloud-based service integration, workflow automation and app sharing.
Microsoft Power Apps Top Uses:
- Build web and mobile applications through text descriptions, PDF documents, sketches or design files.
- Integrate AI capabilities into existing applications with Microsoft Copilot.
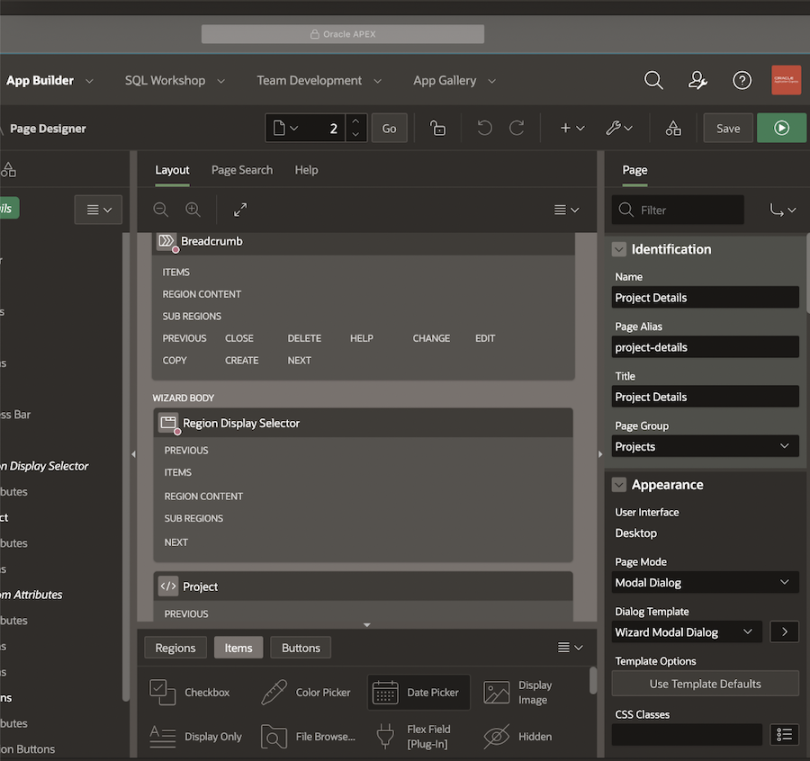
Oracle APEX
Oracle APEX (Application Express) is a low-code platform that requires little to no coding for many situations. Developers have access to professional-looking templates, drag-and-drop tools and a built-in Advisor that assess applications. Oracle claims that the APEX platform automates 98 percent of the coding process, so even beginners with no knowledge of HTML or CSS can create and customize high-quality apps.
Oracle APEX Top Uses
- Quickly build web-based applications with unique data structures and sample data.
- Transform spreadsheets into secure databases with browser-based and easy-to-use UI.
OutSystems
Honda, Mercedes Benz, Intel and thousands of other companies in the tech, automotive and finance industries use OutSystems to build enterprise-grade applications that are tailored to their own specific needs. Its low-code development services allow users to design applications for everything from customer experience optimization to revenue tracking without the need for extensive coding knowledge. OutSystems also claims to be the only platform to combine minimal coding with advanced mobile capabilities, enabling users to visually develop entire application portfolios that can integrate with existing systems.
OutSystems Top Uses:
- Build custom applications with custom behaviors and prebuilt UI elements.
- Inject custom code in certain areas for greater customization.

Pegasystems
Pegasystems is considered to be a leader in both no-code and low-code development, and has integrated them both into its suite of solutions. Its low-code Factory allows virtually anyone within a company to build and deploy their own apps, even if they have little to no coding experience, which frees up time for the company’s developers to work on bigger projects. “Low code and no code are power tools,” Pegasystems’ senior director of product and marketing Anthony Abdulla told Built In in a 2019 interview. “You can do full-featured applications for complex builds as confidently as you could with a coding tool and as rich and robust as you could with a coding tool.”
Pegasystems Top Uses:
- Create custom AI applications for customer service automation.
- Analyze data points to provide custom user experiences across multiple channels.
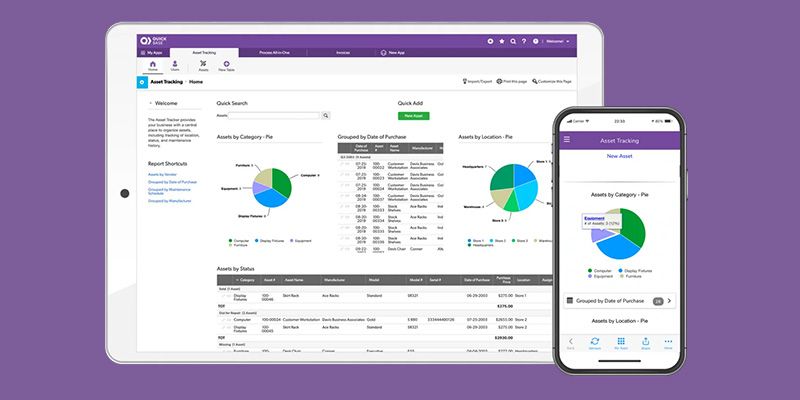
Quickbase
People of all coding experiences can use Quickbase to customize hundreds of pre-built apps, or create their own to help with everything from workflow automation to task management to data integration. The company claims it has nearly 6,000 customers, including 80 percent of the Fortune 50.
Quickbase Top Uses:
- Build custom dashboards and interfaces using a library of pre-built templates.
- Automate repetitive tasks and processes by consolidating external data sources.
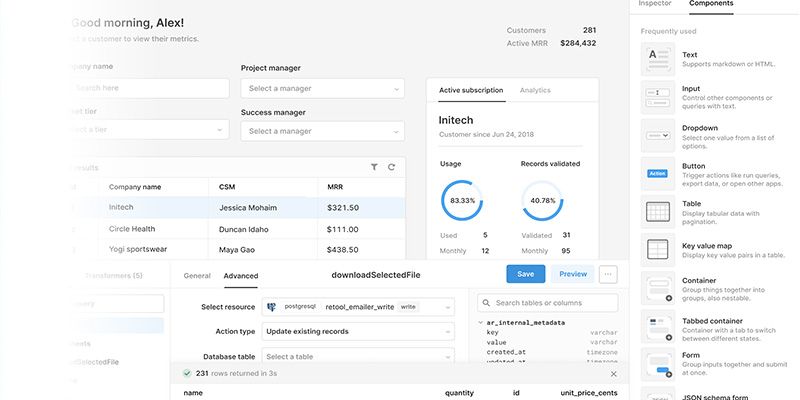
Retool
Retool helps companies like Amazon, DoorDash and Peloton build internal applications in as little as 30 seconds using pre-built, drag-and-drop templates. After selecting a template, users can connect their frontend to a database and build using that information. Unlike other low-code platforms, Retool allows users to switch to code at nearly any time in order to customize how the apps look and function.
Retool Top Uses:
- Build data-heavy applications using drag-and-drop capabilities and pre-built templates.
- Customize the look and feel of apps by writing custom JavaScript and SQL.
SAP
SAP offers techie solutions to just about every business operation, and its platform includes several no-code and low-code features, including SAP Business Application Studio, SAP AppGyver and SAP Process Automation. The SAP Business Application Studio offers both a full-stack development environment and a low-code option to build applications with visual programming. A global, multi-billion dollar company in its own right, SAP is a longtime strategic partner of Google Cloud, and has expanded this relationship.
SAP Top Uses:
- Low-code application builder with useful debugging tools and built-in Git support.
- Seamless integration with other SAP products.
ServiceNow
ServiceNow has been named a leader in the enterprise low-code platforms sector, and for good reason. The company’s App Engine Studio allows developers of various skill levels to work together in a configurable coding environment, but teams can still establish guardrails to determine who has access to different resources. To manage projects and processes, teams can maintain a bird’s-eye view with the App Engine Management Center.
ServiceNow Top Uses:
- Create custom automation workflows and AI tools using a visual design interface.
- Integrate AI agents and customer support specialists into a complementary workflow on a singular platform.
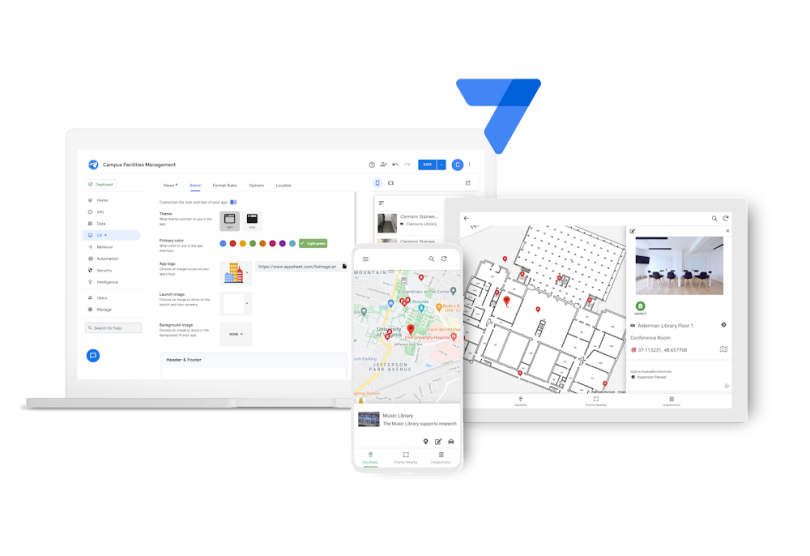
Google AppSheet
AppSheet is Google’s proprietary no-code platform for building custom applications and automations. Using Gemini, a generative chatbot, developers can describe the type of app and features they are looking for and the platform will automatically build it. Some of these include AI tools, custom UI designs, automated push notifications and database connections.
AppSheet Top Uses:
- Build custom applications using basic text inputs.
- Develop AI tools, custom UI designs, automated push notifications, database connections and more.
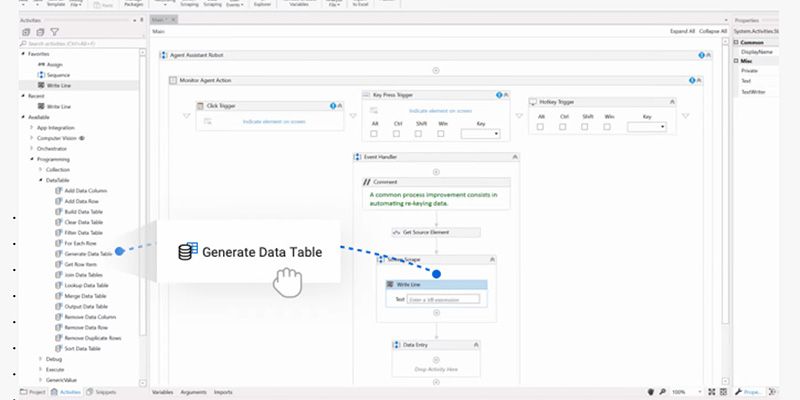
UiPath
UiPath is best known for its automation platform, which uses machine learning and bots to help companies expedite their administrative tasks. In 2020, the company unveiled its “robot-powered” low-code platform, providing yet another way for businesses to build and deploy apps that can connect to all of their legacy software, even if they don’t have APIs.
UiPath Top Uses:
- Create rule-based AI applications to automate repetitive tasks.
- Automate tasks for non-API-based applications and legacy systems.
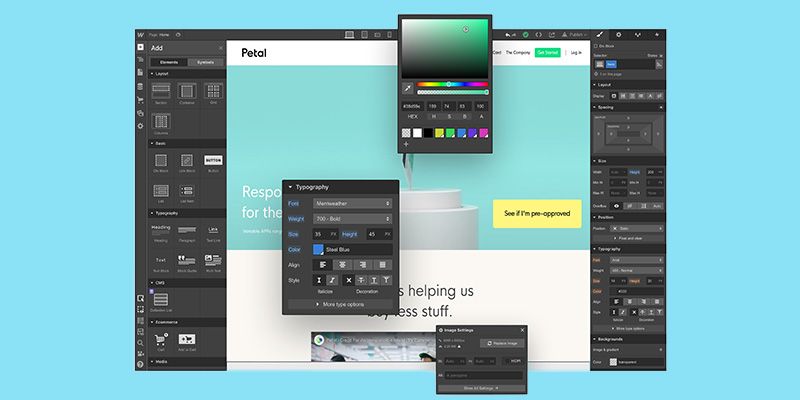
Webflow
With millions of users and a valuation of $4 billion, Webflow has made a name for itself mainly as a no-code development tool, allowing designers to create whatever website they want without having to write a single line of code. But, according to the company, many creators with some coding skills use Webflow as a low-code platform too, making tweaks to the code behind its pre-made templates and drag-and-drop interface for further customization.
Webflow Top Uses:
- Control all aspects of UI design with visual editor and HTML, CSS and JavaScript coding options.
- Publish and edit sites directly from Webflow editor.
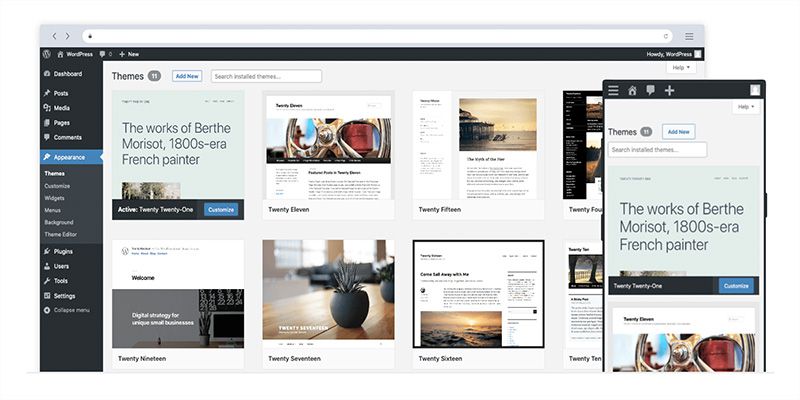
WordPress
Likely another familiar name, WordPress is a publishing software that lets users create custom websites and blogs with a variety of templates. The company claims 43 percent of the web is built with WordPress, making it the world’s most popular website builder. While developers can use the platforms to code custom websites, it also features a range of plug-and-play themes and integrations to build blogs and e-commerce sites.
WordPress Top Uses:
- Build blogs and other sites with premade themes and plug-ins.
- Launch e-commerce sites and leverage marketplace integrations.
Zoho Creator
Beyond popular offerings like its customer relations management system and its business management software, Zoho has created a low-code application development platform that helps users design, develop and run any business software they need. Known as Zoho Creator, the platform provides a scalable, cost-effective way for businesses to build custom applications, monitor their performance with analytics and automate their business processes so that complex issues can be more easily resolved.
Zoho Creator Top Uses:
- Build internal business tools that measure KPIs with little or no-code writing.
- Fast development of customer portals for areas such as companies policies and FAQs.
InterSystems
The InterSystems IRIS platform is an enterprise-grade, low-code software solution that simplifies the design, integration and automation of applications for industries like healthcare. Its drag-and-drop graphical tools enable data transformation, API lifecycle management and business-process orchestration.
InterSystems Top Uses:
- Enable real-time access to data.
- Build smart data fabrics and API-driven services.
- Support generative AI or ML pipelines.
Superblocks
Superblocks’ AI-powered low-code platform helps businesses build internal applications and streamline workflows through tools like its recently launched AI agent, Clark AI, which enables engineering teams to build quickly and securely. Headquartered near Union Square in New York City, the company is currently hiring for a variety of positions.
Superblocks Top Uses:
- Build internal applications with minimal coding.
- Streamline workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a low-code platform?
A low-code platform provides development tools where users can build custom applications with minimal coding. They provide graphical user interfaces, drag-and-drop features, pre-built components and sometimes chatbot-style guidance, making it easier to get a program or website up and running without requiring extensive programming skills.
What is an example of a low-code platform?
Popular low-code platforms include Airtable for database apps, Webflow for responsive web design, and WordPress for blog and e-commerce sites.
What are some benefits of using low-code platforms?
The biggest advantage of low-code platforms is their ability to help companies — especially startups — launch new applications. By minimizing the need for extensive code, these platforms can also reduce development costs.
What are the disadvantages of using low-code platforms?
While low-code platforms can speed up development time and reduce costs, they also have certain limitations:
- Limited customization: Unique features may require traditional coding.
- Performance issues: Applications that require large amounts of data may not run as efficiently as custom-built platforms.
- Security concerns: Third-party applications often include privacy policies, which could grant them access to external data.
Is Salesforce a low-code platform?
Yes, Salesforce is considered a low-code platform. It provides drag-and-drop tools and a visual interface to help users build apps and custom workflows without writing code. However, Salesforce also supports traditional development for more advanced customization.
Is Jira a low-code platform?
Jira is not a low-code platform, as it is primarily used for issue tracking and project management. However, it does include some low-code features, such as the Jira Automation tool, which allows users to create custom automations without any coding.
When not to use a low-code platform?
While low-code platforms can be useful tools for prototyping and rapid development, they can quickly become a hindrance if not used properly. Because these tools are developed for general purpose use, they often lack advanced customization features, making all its custom apps have a similar feel. Furthermore, low-code platforms may not be ideal for applications with large data sources, as it can limit future scalability.




