In Python, dictionaries are ordered data structures that map keys to values. After defining a dictionary, it’s possible to add or update key-value pairs.
What Is a Python Dictionary?
Python dictionaries are ordered data structures that map keys to values. Dictionary keys can be any immutable data type, such as numbers, strings, tuples, etc, while dictionary values can be just about anything from integers to lists, functions, strings, etc. Dictionaries are written within curly brackets {}.
This Python dictionary tutorial covers:
- How to define a dictionary.
- How to access values and check for keys in a dictionary.
- How to add, update and delete keys from a dictionary.
- Dictionary methods.
- How to iterate through a dictionary.
With that, let’s get started.
How to Define a Dictionary in Python
Dictionaries are written within curly brackets {}.

# Define a dictionary code
webstersDict = {'person': 'a human being',
'marathon': 'a running race that is about 26 miles',
'resist': 'to remain strong against the force',
'run': 'to move with haste; act quickly'}While the dictionary webstersDict used strings as keys in the dictionary, dictionary keys can be any immutable data type (numbers, strings, tuples, etc). Dictionary values can also be just about anything (integers, lists, functions, strings, etc).
For example, the dictionary below, genderDict has ints as keys and strings as values.
# Define a dictionary
genderDict = {0: 'male',
1: 'female'}It’s important to know that if you try to make a key a mutable data type (like a list), you will get an error.
# Failure to define a dictionary
webstersDict = {(1, 2.0): 'tuples can be keys',
1: 'ints can be keys',
'run': 'strings can be keys',
['sock', 1, 2.0]: 'lists can NOT be keys'}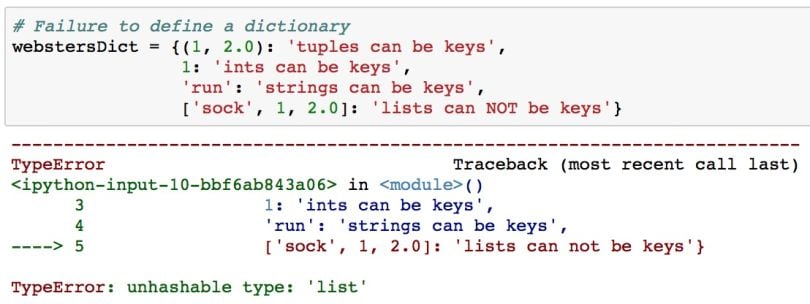
How to Access Values and Check for Keys in a Python Dictionary
Access Values in a Dictionary
To access a dictionary value, you can use square brackets [].
For example, the code below uses the key ‘marathon’ to access the value ‘a running race that is about 26 miles’.
# Get value of the 'marathon' key
webstersDict['marathon']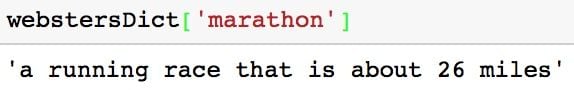
Keep in mind that you will get a KeyError if you try to access a value for a key that does not exist.
# Try to get value for key that does not exist
webstersDict['nonexistentKey']
In the dictionary methods section, you will see the utility of using the dictionary method get() to avoid KeyErrors.
Check If a Key Exists in a Dictionary
You can check if a key exists in a dictionary before trying to access it by using the in operator. The operator will return True if the key exists and False if it does not. For example, say we want to check if the key ‘marathon’ exists in the webstersDict dictionary, we would use the code:
print('marathon' in webstersDict)
#Output: True
How to Add, Update and Delete Keys from a Python Dictionary
Add or Update a Key
You can add a new key-value pair.
# add one new key value pair to a dictionary
webstersDict['shoe'] = 'an external covering for the human foot'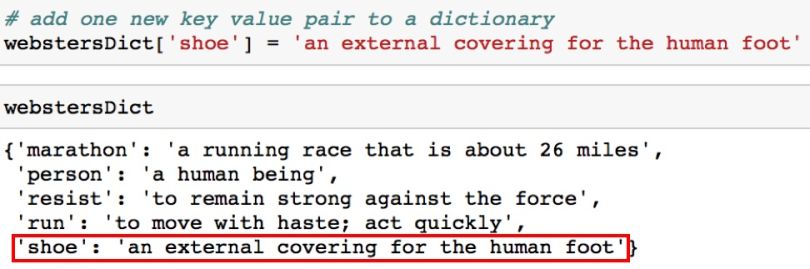
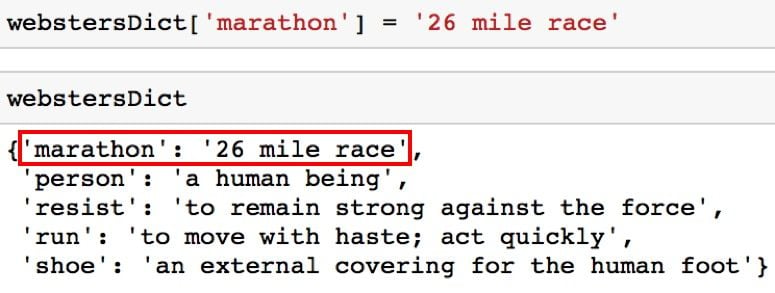
You can also update a key-value pair.
In the dictionary methods section, you will see that you can also add or update multiple key value pairs at a time using the dictionary update method.
Delete Keys from a Dictionary
It is possible to remove a key and its corresponding value from a dictionary using del.
# Remove the key 'resist' from the dictionary
del webstersDict['resist']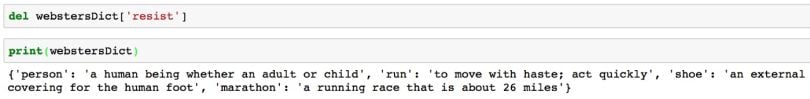
In the dictionary methods section, you will see that you can also delete keys using the dictionary pop method.
Python Dictionary Methods
Python dictionaries have different methods that help you modify a dictionary. This section of the tutorial just goes over various python dictionary methods.
Update Method
The update method is very useful for updating multiple key values pairs at a time. It takes a dictionary as an argument.
# Using update method to add two key value pairs at once
webstersDict.update({'ran': 'past tense of run',
'shoes': 'plural of shoe'})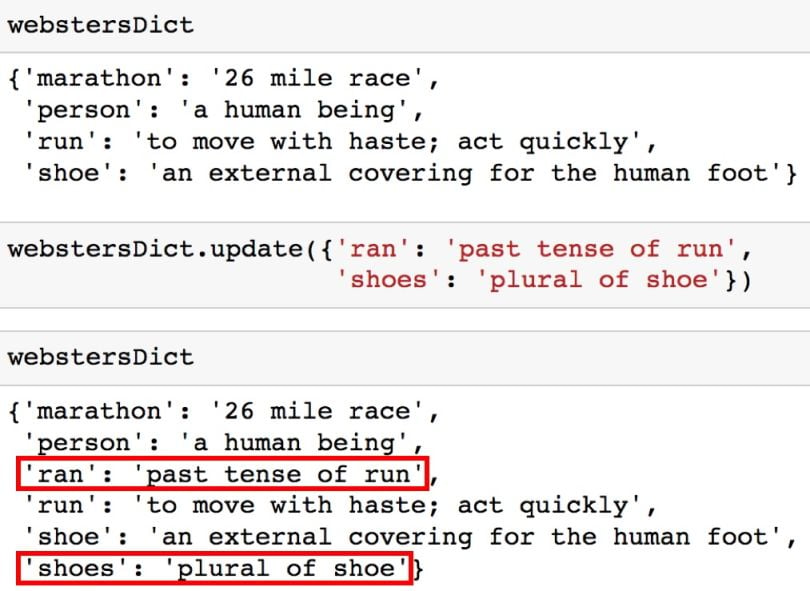
Get Method
# Define a dictionary
storyCount = {'is': 100,
'the': 90,
'Michael': 12,
'runs': 5}The get method returns a value for a given key. If a key doesn’t exist, the dictionary will by default return None.
# Since the key 'Michael' exists, it will return the value 12
storyCount.get('Michael')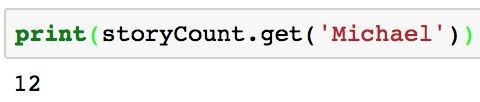
This method is very useful for looking up keys that you don’t know are in the dictionary to avoid KeyErrors.

You can also specify a default value to return if the key doesn’t exist.
# Make default value for key that doesn't exist 0.
storyCount.get('chicken', 0)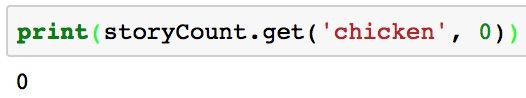
You can see the usefulness of this method if you try a Python Word Count.
Pop Method
The pop method removes a key and returns the value.
storyCount.pop('the')
Keys Method
The keys method returns the keys of the dictionary.
storyCount.keys()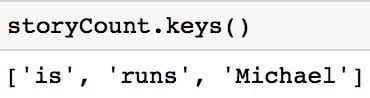
Values Method
The values method returns the values in the dictionary.
storyCount.values()Items Method
The items method returns a list-like object of tuples in which each tuple is of the form (key, value).
webstersDict.items()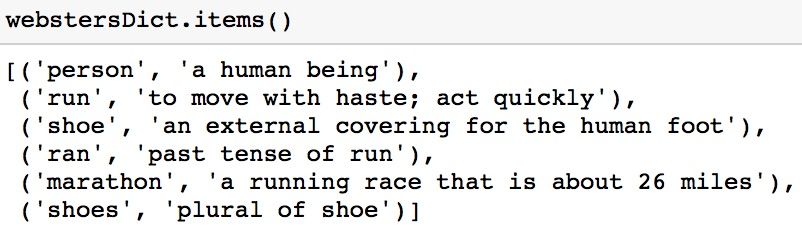
How to Iterate Through a Python Dictionary
You can iterate through the keys of a dictionary by using a for loop.
for key in storyCount:
print(key)
You also iterate through the keys of a dictionary by using the keys method.
for key in storyCount.keys():
print(key)
The for loop below uses the items method to access one (key, value) pair on each iteration of the loop.
for key, value in webstersDict.items():
print(key, value)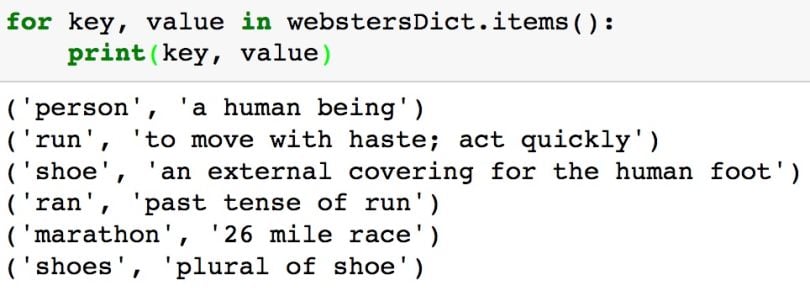
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you define a dictionary in Python?
A Python dictionary is defined using curly brackets ({}) with key-value pairs. For example:
webstersDict = {'person': 'a human being', 'marathon': 'a running race'}
Can Python dictionary keys be any data type?
No, Python dictionary keys must be immutable data types (e.g., numbers, strings, tuples). Mutable data types like lists cannot be dictionary keys.
How do you access a value in a Python dictionary?
To access a value in a Python dictionary, use square brackets ([]) with the associated key. For example:
webstersDict['marathon'] # Returns 'a running race'





