SQL data types are used to specify the type of data that a column or variable can store. While there is some overlap with data types in general-purpose programming languages such as Python or Java, SQL data types have their own unique features and usage.
3 SQL Data Types
Character/string data types are used to store alphanumeric characters in a database.
Numeric data types are used to store numeric values in a database.
Data and time data types are used to store date and time values in a database.
We will discuss the various SQL data types, including character/string data types, numeric data types, date and time data types, Unicode character/string data types, binary data types, and a few other SQL data types.
Let’s consider an example of a single weather table where each row represents a daily weather record in a specific city.
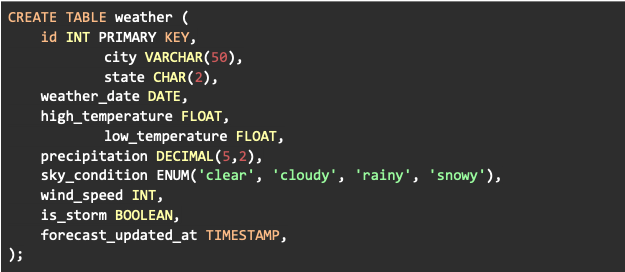
SQL Character and String Data Types
SQL character/string data types are used to store alphanumeric characters in a database. The most commonly used of these are CHAR and VARCHAR. The CHAR data type is used to store fixed-length strings of characters, while the VARCHAR data type is used to store variable-length strings. When adding a VARCHAR or CHAR variable, you specify the maximum number of characters allowed.
The “state” variable in our weather is a great candidate for CHAR(2), because we can represent each state with a 2-letter code. CHAR data are always stored using the same number of characters. If a shorter string is entered, it will be padded to the right with spaces. When string length is uniform or nearly uniform, CHAR can be a better choice because 1) it does not require storing the length data in each record and 2) length does not need to be calculated when reading and writing data. On the other hand, if the string length is more variable (such as for our city column), the VARCHAR type can lead to less wasted disk space.
Numeric Data Types
SQL numeric data types are used to store numeric values in a database. The most commonly used numeric data types are INT and FLOAT. The INT data type is used to store whole numbers, while the FLOAT data type is used to store decimal numbers. The INT data type can store values ranging from -231 to 231-1. For larger numbers, we can use the BIGINT data type which can store values ranging from -263 to 263-1. For our weather example, INT works for the wind_speed variable as long as we do not need decimal precision.
The FLOAT data type can store decimal numbers with a precision ranging from 7 to 23 digits, depending on the specific kind of FLOAT used. While it provides a broad range of values, it doesn’t guarantee exact precision. If we want to store decimal numbers with a higher precision, we can use the DECIMAL or NUMERIC data type. These data types allow us to specify the precision and scale of the decimal numbers, which means that we can control the number of digits before and after the decimal point.
In general, you should use DECIMAL when you need to ensure precise decimal values with no approximation and FLOAT when you have a large range of values and approximation is acceptable.
Date and Time Data Types
Dates and times in SQL are typically stored using DATE, TIME, DATETIME and TIMESTAMP. The DATE data type is used to store a date value in the format of “YYYY-MM-DD”, the TIME data type is used to store a just time value in the format of “HH:MM:SS”, and the DATETIME data type is used to store both date and time values in the format of “YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS”.
TIMESTAMP is generally in a similar format as DATETIME. TIMESTAMP is converted to and stored as UTC in the database — although this depends on the type of database — as opposed to DATETIME where this conversion does not happen. This difference can be important if the database is used across time zones. If we need to calculate the difference in times across time zones (e.g. in two different records or between a record and the “current” time), TIMESTAMP is likely the better option.
Unicode Character/String Data Types
If you want to use symbols from other languages, such as if we want to extend our weather table to include worldwide city names, we need to consider how to use Unicode characters. In some database management systems like SQL Server, there are specific data types like NVARCHAR and NCHAR (analogous to VARCHAR and CHAR) that store Unicode characters. In others, like MySQL, the character set of CHAR and VARCHAR columns can be specifically set to include specific UTF encodings.
Binary Data Types
Binary data, such as images, gifs, PDFs and audio files, can be stored using different binary data types. The most commonly used binary data types are BINARY, VARBINARY and BLOB. The differences between binary types are beyond the scope of this piece, but in most cases it’s more ideal to use the filesystem rather than the database for storage.
Other SQL Data Types
In addition to the data types mentioned above, SQL also has several other data types that are used for specific purposes. For example, the BOOLEAN data type is used to store true or false values, the ENUM data type is used to store one of a predefined list of values (see sky_condition in our example), and the SET data type is used to store a set of multiple predefined values.
Understanding the SQL data types is an important aspect of managing and manipulating data in relational databases. For starting with SQL, knowing the basics of numeric, character and date/time data types will suffice. A more advanced understanding of the tradeoffs between specific data types is needed as the database grows and efficiency and storage become more critical.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between VAR and VARCHAR in SQL?
In SQL, CHAR is used to store fixed-length strings of characters, adding spaces to lengthen values as needed. Meanwhile, VARCHAR is used to store variable-length strings of characters to preserve space as needed.
When should I use FLOAT vs. DECIMAL in SQL?
In SQL, FLOAT produces a wide range of values, although it can lead to precision errors. As a result, it’s best to use FLOAT when approximation is allowed. DECIMAL is better when greater precision is required.
What data type should I use for storing large numbers?
When dealing with larger whole numbers, BIGINT is a convenient option. This data type can handle values ranging from -263 to 263-1.





