The rise of augmented reality and virtual reality is forever changing the way health professionals treat and care for their patients.
How Is VR/AR in Healthcare Used
- Helping providers become more empathetic toward patients.
- Teaching communication skills in people with autism.
- Gamifying physical therapy and rehabilitation.
- Providing more effective mental health treatments.
- Detecting visual impairments.
- Organizing medical records.
- Enabling more efficient surgeries and procedures.
- Enhancing medical training.
- Expanding the capabilities of telemedicine.
- Improving memory and cognitive function treatments.
VR in healthcare is used for many purposes. The technology enables surgeons to virtually examine a patient before a procedure, allows medical personnel to train in life-like simulations and supports virtual sensory tests for patients with muscle weakness. VR is also used to generate empathy among healthcare providers by simulating the conditions of their patients.
That last use case is what inspired Carrie Shaw to enter the healthtech industry and launch Embodied Labs. As a 19-year-old, Shaw struggled to understand the everyday experiences of her mother, who suffered from early-onset Alzheimer’s disease and a visual impairment. To ensure she and others would properly care for her mother, Shaw took a pair of safety goggles and covered the left half of each lens with blue tape to mimic her mother’s partial blindness.
“That really helped me understand how to care for her,” Shaw said. “It was very memorable to see what she was seeing, and feel where my body was unprotected.”
It can be easy to forget the everyday challenges that patients must live with, which is why companies like Embodied Labs employ VR to encourage empathy among health professionals. And this is just the beginning. From effectively treating trauma to organizing medical records, AR and VR in healthcare are improving provider-patient interactions in various ways.
10 VR/AR in Healthcare Applications
VR in healthcare is making it easier for many medical professionals to conduct surgeries, educate patients, facilitate rehab therapy and take care of back-office work. To give you a snapshot of how companies are helping make that happen, we rounded up a list of a few standout VR in healthcare applications.
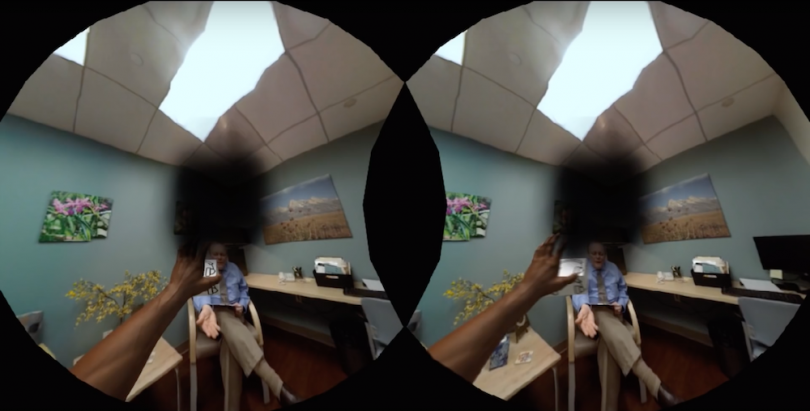

1. Fostering Empathy Among Healthcare Professionals
The immersive nature of VR makes it easier to see life from someone else’s point of view, which creates empathy. That’s why Embodied Labs develops interactive, 360-degree virtual reality videos where users can experience a patient’s perspective.
In one of the company’s first labs, users become Alfred, a 74-year-old man suffering from macular degeneration and high-frequency hearing loss.
“Students would put on the headset, and even though they would read in their introduction that they were about to embody Alfred, they would immediately say, ‘There’s something broken, I can’t see.’ Or, ‘Turn up the volume, I can’t hear,’ and then realize [that was the point],” Shaw said.
Another simulation lets users take on the life of Beatriz, a woman with Alzheimer’s. Wearers are prompted to answer questions or ask for help, but the words emerge jumbled. Another part of the Beatriz experience simulates a stressful environment in a crowded room. Sound becomes distorted and volume increases. As Alzheimer’s also adversely affects communication, this is an important part of understanding the overall experience.
These interactive experiences can help caregivers be more mindful of the effects of a condition and how it influences a patient’s behavior, allowing them to more specifically respond to their needs.
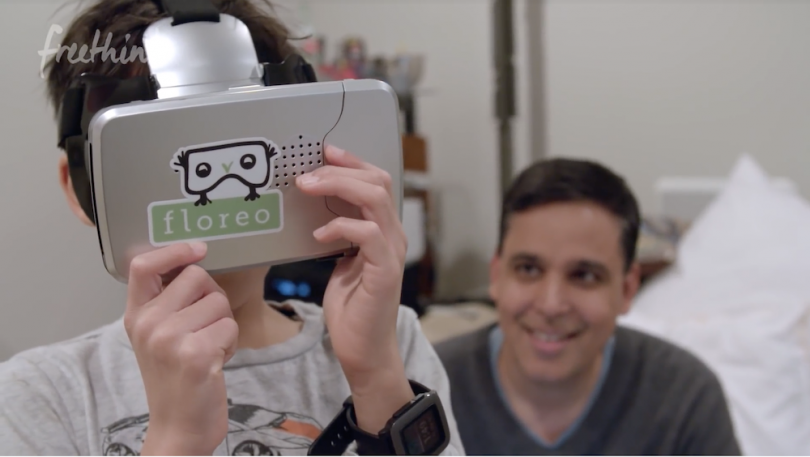

2. Teaching Communication Skills to People With Autism
Consider the case of Vijay Ravindran and his wife Vibha Sazawal, whose son Manoj was diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder.
From an early age, Manoj displayed an intense interest in maps and navigation. He especially liked to explore Google Maps. When Google Street View for VR debuted, Ravindran let Manoj try it out. The result: love at first sight.
Seeing Manoj interact with VR inspired Ravindran and Sazawal to start Floreo, which uses virtual reality to teach social and communication skills to people with autism. Floreo’s platform includes games and activities that explore social connections, situational training and calming techniques.
“Traditional therapy is delivered in an office or in the home in a pretty constrained environment,” Ravindran said. “In virtual reality, we can create environments that suit the situation.”
Some of Floreo’s games help kids practice skills like imitation, nonverbal gestures or joint attention. Other activities immerse them in real-world scenarios, like crossing a busy intersection or interacting with law enforcement.
“For kids with autism who are often overwhelmed by the complexity, noises and visual distractions of the real world, it allows them to see a simpler world to operate in and then practice the skills we’re trying to teach,” Ravindran said.
3. Gamifying Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Besides making rehab and physical therapy more engaging for patients, VR and gaming technology also has a positive impact on training muscles like those in parts of the shoulder and wrists.
InMotion has taken this method and embraced a therapy model centered around VR in healthcare and gamification. The company’s Corpus VR platform allows doctors to gather motion data while patients participate in virtual games. Health professionals can control the degree of difficulty for each level, challenging patients to work harder at a reasonable pace.
4. Providing More Effective Mental Health Treatments
VR in healthcare has become a convenient mental health tool for treating patients with phobias. Through simulations, providers can expose patients to a fearful object or situation in controlled doses, building up their tolerance over time. This concept can also be extended to more serious conditions, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The University of Southern California has explored VR’s potential to treat PTSD through its project Bravemind, which applies VR simulations to treat military veterans and sexual assault survivors with PTSD. Users are gradually reintroduced to settings that force them to confront memories and emotions they’ve suppressed. They are also asked to narrate what they remember, and health professionals can influence the virtual environment to reproduce an event or action as the user recounts it.
By facing triggering situations in manageable increments, patients with PTSD can come to accept their past experiences and reduce their PTSD symptoms in the process.
5. Detecting Vision Impairment
SyncThink uses VR goggles with eye-tracking abilities to test for visual impairments. The company’s Eye-Sync platform helps test for concussions soon after a person sustains a bad blow to the head. Eye-Sync even won a Breakthrough Device Designation award from the FDA.
6. Accessing Medical Records
Augmedix uses augmented reality in healthcare and Google Glass to give doctors quick access to a patient’s electronic health records. In addition to conveying information like previous visits and current medications, Google Glass also acts as a scribe that records important information from each appointment, consequently facilitating a more natural doctor-patient interaction.
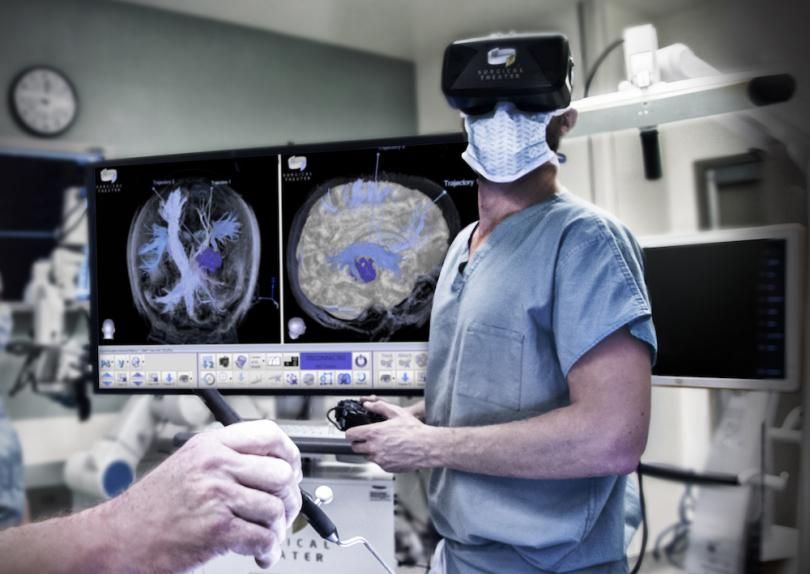
7. Preparing for Surgery
Surgical Theater adapts MRIs, CT scans and other 2D medical imaging techniques into a 3D model. Surgeons can then use VR to explore and interact with this 3D model to plan a surgery or update a patient on the process.
8. Enhancing Medical Training
Surgeons aren’t the only ones who benefit from VR technologies. Nurses and first responders need to have sound decision-making skills and thorough knowledge of health procedures. That’s why companies like SimX and VRpatients have developed simulations that train medical personnel via life-like scenarios.
Both these platforms offer reporting and grading tools, so educators can assess how learners apply their knowledge while under pressure.
9. Expanding the Capabilities of Telemedicine
Telemedicine has become essential as more patients have come to rely on virtual visits, and VR has taken this method to the next level. VR in healthcare makes it possible for doctors to conduct sensory tests on patients with motor impairments, such as muscle weakness in stroke patients.
Companies are introducing VR into telemedicine, with XRHealth being a prime example of this shift. The company combines a VR headset and entertaining games to get patients to perform movements that target specific areas of the body. Through XRHealth’s physio series, patients can exercise muscles in their upper back, neck and shoulders.
10. Improving Memory and Cognitive Function Treatments
The advantages of VR and gaming in healthcare goes well beyond being entertaining. In fact, some researchers believe VR games can boost one’s memory, and e-learning companies are buying into the technology.
Librarium pairs engaging lessons with virtual environments and memory palace techniques, aiming to create learning experiences that are more engaging and personalized for students. The hope is that students can better retain knowledge while feeling more comfortable learning in online environments.

Future of VR/AR in Healthcare
As impressive as it may seem now, VR is a rapidly advancing technology. Every year sees the release of powerful new headsets and innovative software. Shaw, for one, thinks her company has only scratched the VR surface.
“I think we’re hitting maybe five percent of the current capabilities of the hardware,” she said. “Everything from the filming techniques to the way you can integrate branching stories and use AI to respond to what you do.”
The interdisciplinary approach of supplementing AR and VR with AI holds promise for the future of VR in healthcare. While the technology is still crucial for crafting immersive and engaging experiences, it’s taking on increasingly complex roles that prove it worthy of being more than a gamification tool.
“There’s a lot of buzz about VR and it being an empathy machine,” Shaw said. “We talk about it like it’s a movie or a game, but it’s really a science. More than just feeling empathy, it’s something that transfers knowledge and [impacts] behavior change.”




