When most people have a question, they turn to a search engine for an answer. Google is still the most popular option by far, but there are plenty of alternatives that emphasize user privacy, offer cutting-edge features and provide unique datasets of information. Plus, the growing popularity of generative AI and ChatGPT has ushered in an entirely new kind of search engine — one that can summarize and even contextualize information from across the web to provide instant answers, no clicking blue links required.
Next time you’re seeking answers, here are some search engines you can try.
Top Search Engines
- Bing
- Yahoo! Search
- DuckDuckGo
- Brave Search
- Perplexity
- Ecosia
- You.com
- AOL
- Ask.com
Mainstream Search Engines
Google is the most popular search engine in the world. Capturing nearly 92 percent of the search market, it’s no wonder why SEO specialists seek out any available piece of information about Google’s ranking algorithm. Google can search for news, images, videos and scholarly articles. Users can also upload images to Google Lens to find matching results. Google now offers generative AI-powered overviews that summarize search results.
Bing
Launched by Microsoft in 2009, Bing is the second most popular search engine. It accounts for roughly 4 percent of overall search volume, but its market share jumps to nearly 12 percent on desktop. Bing has a suite of AI features as well, including “knowledge cards” that enrich each query with additional information. Copilot has also been integrated into Bing, so users can quickly access the chatbot to address more complex questions and prompts.
Yahoo! Search
Yahoo! Search was one of the first popular search engines. These days, its market share is just over 1 percent, or around 3 percent on desktop. Yahoo’s search engine is powered by Bing and is compatible with common web browsers, including Edge, Safari, Firefox and Chrome. Like Microsoft and Google, Yahoo augments its search engine with email, news and other content while featuring trending stories on its front page for added convenience.
Privacy-Focused Search Engines

DuckDuckGo
DuckDuckGo launched in 2008 with a focus on user privacy. The company said it does not track user’s searches, and it aims to block trackers across the web through its app and browser extensions. Because it doesn’t track and store individual user data, DuckDuckGo said its search results are not personalized and therefore avoid the “filter bubble” that can occur when search engines limit search results to those they think the user would like to see. DuckDuckGo also allows users to access top AI models made by companies like Anthropic, Meta, Mistral and OpenAI, while still maintaining their data privacy.

Brave Search
Brave Search is another search engine that doesn’t collect a user’s personal information or search history, but it differentiates itself from the competition with a companion browser that blocks trackers from collecting users’ data across the web. While other alternative search engines often borrow search capabilities from bigger players, Brave Search claims it uses an independent search index. Accessible on any web browser, Brave Search also offers AI-generated responses to provide users with quick answers to their queries.

Startpage
Startpage is another privacy-focused search engine that serves up search results from Google without storing users’ personal information, search data or IP addresses. As a result, users can search the web without worrying about price trackers, retargeted ads and third parties building personal data profiles. It goes a step further with its “anonymous view” feature, which allows users to visit websites anonymously, essentially acting like a VPN.
AI Search Engines
Perplexity
Perplexity combines conversational AI with search, allowing users to enter prompts and refine their results with follow-up prompts. Known as threads, these conversations are then stored in a library where users can revisit previous inquiries and responses. Users can also explore topics in more depth with Perplexity’s Pro Search, which uses follow-up questions, summaries and a variety of sources to deliver a more personalized search experience.
You.com
You.com’s primary feature is an AI chatbot that searches the web to retrieve answers to users’ search queries. Users can also search through more traditional means, filtering results to find images, videos, news and public social media posts. The platform offers three AI chat searches per day through its free version, and it allows unlimited searches on its premium version.
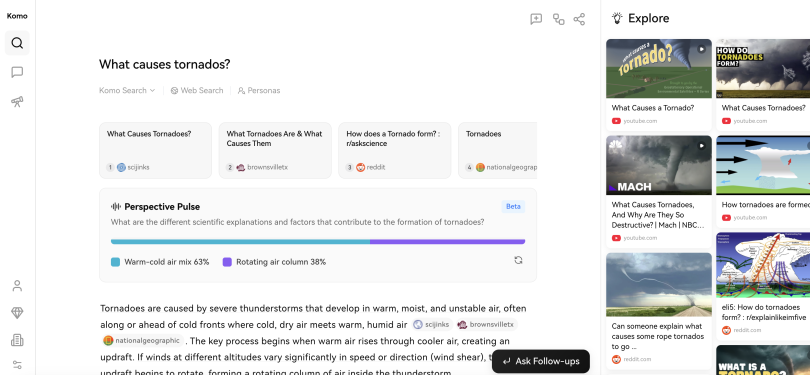
Komo
Komo is an ad-free search engine powered by a variety of models, including GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet. It can be set to four different modes: Ask, Research, Search and Explore. With Ask, users get AI-generated responses to any question they ask, along with relevant links to sources found on the web; ; Research, which is only available to paying customers, provides AI-generated topic analyses, along with citations; Search works more like a regular search engine, providing a list of relevant links but no summaries; and Explore only offers links to videos in response to user queries.
International Search Engines
Yandex
Yandex is a Russian-based search engine that enjoys 67 percent of Russia’s market share, doubling Google usage in its home country. It is also popular in several other neighboring countries. In addition to its search engine, Yandex provides users with easy access to email, weather, maps, games and translation services. It also offers a suite of developer tools, including its search engine tools Yandex XML and turbo pages.

Baidu
Baidu is the most-used search engine in China, capturing 52 percent of the country’s market share. Baidu’s ranking algorithm prioritizes websites that are hosted on Chinese servers, and it only indexes simplified Mandarin characters. The search engine has introduced new algorithms over the years to improve the user experience, and trends like Chinese users trusting bigger brands over other companies influence Baidu’s search results as well.

Qwant
Qwant is a privacy-focused French search engine that builds its own index, supplementing results with Bing. Its trackerless service avoids targeted ads, does not resell users’ personal data and is designed to refrain from putting bias into its search results. With regional values around data sovereignty built in, Qwan positions itself as a European alternative to more mainstream American sites like Google.
Other Search Engines
Ask.com
Originally known as Ask Jeeves, Ask.com was founded in 1996 and gets its name from the butler Jeeves, a fictional character in P.G. Wodehouse’s books. While the business became known for the question-and-answer community it tried to create, it has since evolved into a more traditional search engine. Users can now submit basic queries and filter their search with topics like culture, lifestyle and movies.

Ecosia
Ecosia, a certified B Corp, is an eco-conscious search engine that donates 100 percent of its profits toward climate action, mostly to tree-planting efforts. The Ecosia website states the company has planted nearly 213 million trees in more than 35 countries. Ecosia, which is powered by Microsoft Bing, also touts its privacy policies and does not create user profiles or sell users’ data. Users can access Ecosia either through its website or through its Chrome browser extension.
Yep
Ahrefs, which develops SEO research tools, launched search engine Yep in June 2022 with the pledge to give 90 percent of its ad revenue to creators and publishers. By sharing its revenue, Yep aims to provide creators and publishers with much-needed revenue, reducing their dependence on paywalls and affiliate links. This new business model could also encourage new creators to join the space. Yep also claims not to store users’ search history or IP addresses.
Dogpile
Dogpile, which was founded by Infospace in 1996, is an example of a metasearch engine that aggregates search results from multiple mainstream search engines, including Google and Yahoo, and delivers the results it deems to be most relevant. Like more mainstream search engines, Dogpile offers searches for news, images, videos and articles while addressing popular searches with its ‘favorite fetches’ section. Dogpile is now owned by System1.
The Wayback Machine
The Wayback Machine unlocks a whole new world of information that is no longer on the internet. This massive digital library, known as Internet Archive, has been maintained since 1996 by a nonprofit organization. While not as easy to navigate as conventional search engines, Internet Archive offers more than 800 billion web pages and millions of books, audio recordings, videos and images that would have otherwise been lost to time.

SearX
Searx is a more modern metasearch engine that emphasizes user privacy. Searx claims not to share users’ information with the search engines it uses. It also allows users to choose which search engines from which it pulls results. The website is also open source, so users are encouraged to look at the source code and improve upon it. This also enables users to develop their own engine models and tailor searx to their specific search needs.

WolframAlpha
WolframAlpha, a computational intelligence engine, is not a typical search engine, but it can be just as valuable when used correctly. It uses a vast library of data, algorithms and equations to calculate answers to complex math, science and linguistic problems across any academic discipline. Most commonly used by students, educators and researchers, WolframAlpha offers a free version as well as premium versions with more advanced features.
AOL
Launched in 1997, AOL’s search engine provides users with an in-depth search that brings up relevant articles, videos and images, among other pieces of information. Users can also narrow down their search by categories, including business, entertainment, games, health and a more upbeat ‘lighter side’ section. AOL is now under the Yahoo! brand as a result of Verizon acquiring the two entities and then selling them to Apollo Global Management.
Is Generative AI Replacing Search Engines?
When it comes to having their basic questions answered, more and more people are turning to generative AI tools like ChatGPT, Gemini and Claude, rather than a traditional search engine. Whether you’re looking for a recipe or searching for a job these systems provide direct, conversational answers without requiring users to sift through multiple links. To keep up, mainstream search engines like Google and Microsoft have integrated AI features of their own.
However, it’s important to remember that generative AI is still prone to hallucinations and bias, producing inaccurate summaries that can mislead users. And though many of these platforms offer citations to address this flaw, they may still cite inaccurate information or make up citations altogether. Artificial intelligence has made great strides in the realm of search, but the full scope of the technology’s potential remains to be seen.
At the moment, the debate over whether AI will supplant traditional search seems less about outright replacement and more about convergence. Traditional search engines are still the primary source of verified, reliable information, while generative AI is becoming the default for fast, synthesized answers. The balance between the two — depth and accuracy versus speed and convenience — is still being negotiated.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a search engine?
A search engine is a tool used for finding information online. It works by continuously crawling web pages and using algorithms to surface the content that’s most relevant to the user’s search query.
What are the most popular search engines?
Google, Bing, Yahoo! and DuckDuckGo are the most popular search engines in the United States.
What are the safest search engines?
For safety-minded users, search engines like DuckDuckGo, Brave Search and Startpage take a privacy-first approach, refusing to collect users’ personal information and taking steps to block trackers.




