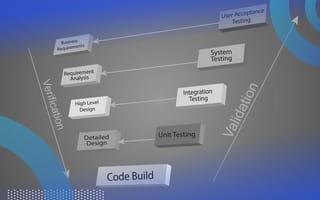
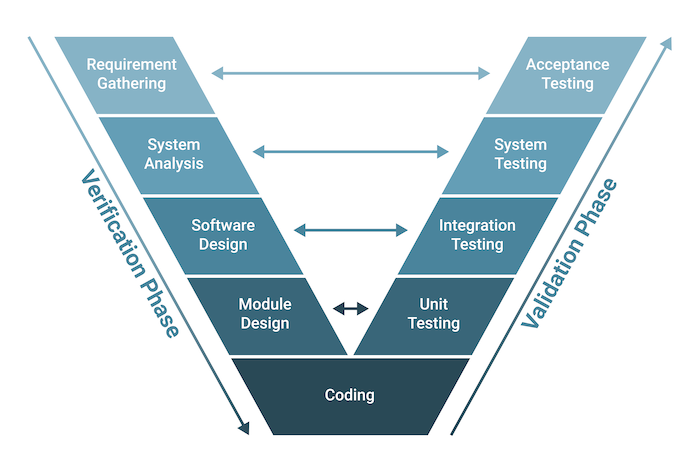
The V-model is named after its shape, which resembles the letter “V.” In the V-model, we divide the software development life cycle into phases and each phase is associated with a corresponding testing phase.
The left-hand side of the V represents the verification phase while the right-hand side represents the validation phase. Verification confirms the product is built correctly according to specifications. Validation confirms the product meets user needs and expectations.
When to Use a V-Model
V-models are used in situations wherein the requirements and understanding of the software’s functionality are well-defined from the beginning. The V-model assumes stable requirements and discourages iteration, so in cases where the project scope is clear and the development team has a solid understanding of the requirements, the V-model can be an effective tool for delivering high-quality software.
The V-model is useful when working with larger teams where communication and coordination between developers and testers becomes challenging. By clearly defining the testing requirements for each stage of the development process, the V-model can ensure that all team members are working toward a shared understanding of the project’s goals and objectives.
V-Model Verification Phases
The verification phase refers to the practice of evaluating the product development process to ensure the team meets the specified requirements.
The verification phase includes several steps: business requirement analysis, system analysis, software architecture design, module design and coding.
1. Business Requirement Analysis
In the business requirement analysis step, the team comes to understand the product requirements as laid out by the customer.
2. System Analysis
In the system analysis step, the system engineers analyze and interpret the business requirements of the proposed system by studying the user requirements document.
3. Software Architecture Design
In the software architecture design stage, this involves selecting software structure based on identified modules, their functions, interface relationships, dependencies, and relevant technical elements like database schema and diagrams. Preliminary integration test strategies are also outlined during the architecture design phase, guiding how modules will later be tested together.
4. Module Design
In the module design stage, the development team breaks down the system into small modules and specifies the detailed design of each module, which we call low-level design.
5. Coding
Finally, we begin coding. The development team selects a suitable programming language based on the design and product requirements. There are, of course, guidelines and standards for coding. The code undergoes multiple reviews to verify logic, performance, security and compliance with coding standards.
V-Model Validation Phases
The validation phase involves dynamic analysis methods and testing to ensure the software product meets the customer’s requirements and expectations. This phase includes several stages including unit testing, integration testing, system testing and acceptance testing.
1. Unit Testing
During the unit testing stage, the team develops and executes unit test plans to identify errors at the code or unit level. This testing happens on the smallest entities, such as program modules, to ensure they function correctly when isolated from the rest of the code.
2. Integration Testing
The integration testing stage involves executing integration test plans developed during the architectural design step in order to verify that groups created and tested independently can coexist and communicate with each other.
3. System Testing
The system testing stage involves executing system test plans developed during the system design step. System test plans are developed by quality assurance (QA) teams using business requirements defined by stakeholders. System testing ensures the team meets the application developer’s expectations.
4. Acceptance Testing
The acceptance testing step is related to the business requirement analysis part of the V-model and involves testing the software product in the user environment to identify compatibility issues with the different systems available within the user environment. Acceptance testing also identifies non-functional issues like load and performance defects in the real user environment.
Principles of V-Model
The V-model emphasizes the importance of testing and quality assurance throughout the entire development process. Here are some of the V-model’s key principles.
Integrate Testing Throughout Development
Testing is not just an activity that happens at the end of the development process. Instead, testing is integrated into every stage of the development lifecycle, from requirements gathering to deployment.
Plan Testing in Parallel With Development
In the V-model, every development stage directly corresponds to a predefined testing phase, ensuring traceability and test coverage. Testing activities are planned in parallel with development activities so that the necessary resources are available to support testing.
Prevent Defects
The V-model emphasizes the importance of preventing defects rather than simply identifying and fixing them after they’ve been discovered.
Develop Clear and Concise Requirements
The V-model places great emphasis on clear and concise requirements. Without a clear understanding of what the software is supposed to do, it’s impossible to develop effective tests or to build high-quality software.
Combine Development and Testing
In the V-model, development and testing are not separate activities. Instead, they are closely integrated and collaboration between developers and testers is critical for ensuring that the software meets the required quality standards.
Advantages of Using the V-Model
- Improves Quality: From the beginning, the V-model ensures that quality is built into the development process, which results in fewer bugs in code and higher-quality software.
- Reduces Risks: The V-model provides a clear roadmap for the entire development process, which allows for better risk management and mitigation.
- Increases Efficiency: The V-model encourages collaboration between different teams and stakeholders, which results in more efficient development and testing.
- Improves Communication: The V-model emphasizes communication between stakeholders, to ensure everyone has a clear understanding of the requirements and objectives.
- Enhances Testing: The V-model places a strong emphasis on thorough and effective testing throughout the entire development process.
- Improves Documentation: The V-model requires comprehensive documentation at every stage of the development process, which leads to better record-keeping and easier code maintenance.
Disadvantages of Using the V-Model
- Rigid: The V-model can be inflexible and provide very little room for changes or deviations from the plan. This rigidity can make it difficult to adapt to changing project requirements or new information.
- Time-Consuming: The V-model can be time-consuming due to its focus on thorough planning and documentation at every stage. These factors can slow down the development process and lead to longer project timelines.
- Resource Intensive: The V-model requires a significant amount of resources including time, budget and personnel, thereby making it a difficult model for small teams or organizations with limited resources to implement.
- Limited Agility: The V-model may not be well suited for Agile development approaches, which rely on flexibility, iterative development and continuous feedback.
- Overemphasis on Testing: While thorough testing is a critical component of software development, the V-Model may place too much emphasis on testing, which can lead to production delays and increased costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the V-model in software development?
The V-model is a software development process where each phase of the software lifecycle is paired with a corresponding testing phase, forming a “V” shape that emphasizes verification and validation.
When should the V-model be used?
The V-model is best used when software requirements are clear and well-defined from the start, and when close coordination between development and testing teams is needed.
What are the verification and validation phases of the V-model?
Verification phases of the V-model (each aimed at ensuring the product is built correctly) include:
- Business requirement analysis
- System analysis
- Software architecture design
- Module design
- Coding
Validation phases of the V-model (all designed to confirm the final product meets user requirements) include:
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- System testing
- Acceptance testing