The JavaScript reduce() method makes dealing with arrays easier. It’s a higher-order function in JavaScript that takes an array and reduces it to a single value. It’s most often used for data manipulation, which was introduced in JavaScript ES6.
What Is Javascript Reduce?
JavaScript reduce() is a higher order function used in data manipulation that reduces an array to a single value. It takes two parameters: a callback function and an optional initial value. The uses for reduce() include calculating the sum or product of all elements, finding the maximum and minimum value, flattening an array and more.
The reduce() method takes two parameters: a callback function and an optional initial value. In the callback function, it takes an accumulator as its first parameter and the value of the current array element as its second parameter. The accumulator is initialized to the first element of an array if no initial value is provided. The callback function performs some operation on the accumulator and the value of the current element, and returns the result, which becomes the new value of the accumulator for the next iteration.
This will be more clear once we run through some code examples. Let’s first discuss how the reduce() method works.
JavaScript Reduce Syntax
The syntax for the reduce() method in JavaScript is as follows:
array.reduce(callback, initialValue); Here, array is the array on which the reduce() method is called. The reduce method returns the final value of the accumulator after iterating over all the elements in the array.
The callback is a required callback function that will be called on for each element of the array. The callback function takes four parameters:
- Accumulator (required): This contains the value calculated from the previous iteration. On the first iteration, if an
initialValuewill be provided, the accumulator will be set to the value ofinitialValue. - currentValue (required): The current value of the element is processed in the array.
- currentIndex (optional): The index of the current element is processed in the array.
- Array (optional): The original array on which the
reduce()method was called.
How to Use JavaScript Reduce
In JavaScript, the reduce() method runs a “reducer” callback function over all elements in the array in ascending-index order, and it accumulates them into a single value. Here’s how to use it:
1. Define the Callback Function
Define the callback function you want to apply to each element of an array. This function should take two arguments: the accumulator (accumulated result) and the next element in the array.
For example, let’s find the sum of all elements in an array. We will create the function add and pass two parameters, i.e., accumulator and current value. The function will return the sum of two values. Here is the code snippet:
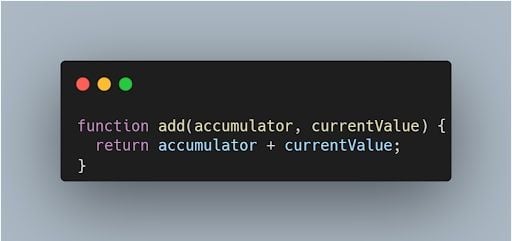
2. Call Reduce()
Then we’ll call the reduce() method on the array you want to apply it to, passing in your function as the first argument.
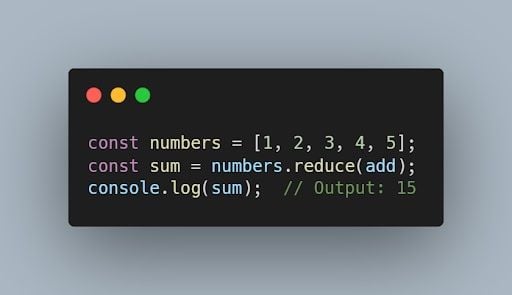
3. Pass an Initial Value
We can also pass an initial value as the second argument to reduce(). This will be used as the starting value for the accumulated result. Here is the code snippet:

The reduce() method works by repeatedly applying the function to the cumulative result and the next element of the iterable, and updating the cumulative result with the return value of the function. This process continues until all the elements of the iterable have been processed and the final result is returned.
The reduce() method is a central concept in functional programming, where it’s not possible to mutate any value. In order to accumulate all values in an array, one must return a new accumulator value on every iteration.
reduce() does not mutate the array on which it is called, but the function provided as callbackFn can. The reduce() method can be used to perform a wide range of operations of an array, such as calculating the sum or product of all elements, finding the maximum and minimum value, flattening an array and more.
4. Return Value
The value that results from running the “reducer” callback function to completion over the entire array.
JavaScript Reduce Examples
Below are some common ways you can use JavaScript reduce(), including:
- Find an average of an array.
- Flatten an array.
- Remove duplicate items in an array.
1. Finding an Average of an Array With JavaScript Reduce()
To find the average of an array using reduce() method in JavaScript, we can first calculate the sum of all elements in the array using reduce() and then divide the sum by the length of the array.
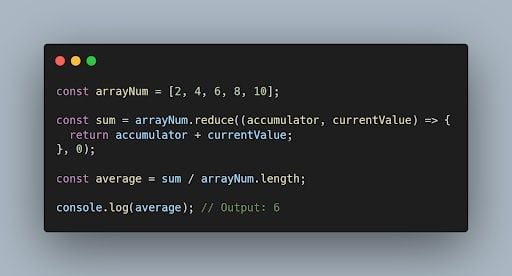
Here is an example to calculate the average using reduce().
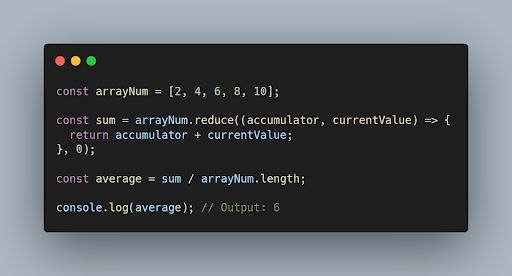
In the above example, we have an array (arrayNum) of integers. Using reduce() method, we are calculating the sum of all the numbers in the array. Zero is the initial value of the sum. To calculate the average, divide the total sum by the length of the array. Finally, we print the average to the console using console.log().
2. Flatten Arrays With JavaScript Reduce()
To flatten the arrays using the reduce() method, we follow the steps:
- Define the multidimensional array that we want to flatten.
- Use the
reduce()method to iterate over the array and concatenate each element to the new array. - Return the flattened array.
Here is an example code snippet:
In the above code, we define a multidimensional array (flattenArrayNumbers) that contains three nested arrays. We use reduce() to concatenate each element of the nested arrays to the new array flattenArrayNumbers. The initial value of accumulator is an empty array, which is passed as the second argument to reduce(). Finally, flattened array output is returned.
3. Remove Duplicate Items in an Array With JavaScript Reduce()
To remove duplicates in an array using the reduce() method, we’ll follow the following steps:
- Define the array with duplicate values.
- Use the
reduce()method to iterate over the array and use theincludes()method to check if the number is already present in the array. Then, we skip the number and add only unique items in the accumulator. - Return the accumulator with unique items.
Here is an example code snippet that demonstrates the above steps:
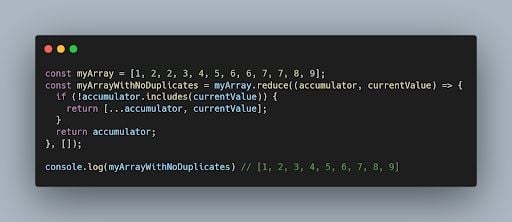
In the above code, we define an array (myArray) that contains duplicate numbers. We then use reduce() to iterate over the array. Using includes(), we check the number to determine if it is already present in the accumulator and return the array with unique items. The initial value of accumulator is an empty array, which is passed as the second argument to reduce(). Finally, a new array with unique elements is returned.
JavaScript Reduce Method Useful Tips and Mistakes
Here are some useful tips to use the reduce() method in JavaScript:
- Always provide an initial value to the accumulator if possible.
- Make sure the callback function is pure. The
reduce()method and callback function should not modify the values of the original array. - Understand the parameters of the callback function. The callback function takes two parameters: the accumulator and the current value of the array being processed.
- Use the accumulator to store the intermediate result. The accumulator is the value that is returned by the callback function and passed as the first argument in the next iteration.
- Use the array function syntax to write concise code. The arrow function syntax makes it easy to write concise and readable code for the callback function.
- Use the reduce() method for iterating through large arrays and converting arrays to one value, and use for loops for iterating over smaller arrays and repeating code until a specific condition is met.
- Remember that the reduce() method doesn’t execute the function for empty elements in an array.
- Remember that at the first callback when using
reduce(), no value is returned from the previous callback.
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using the reduce() method in JavaScript:
reduce()should be used to return a new value based on the inputs, not to modify the original array or external state.- Modifying the original array or external state inside the callback function.
- Nesting too many operations inside the callback function.
- Not understanding the parameters of the callback function.
- Not providing the initial value to the accumulator.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is reduce in JavaScript?
The reduce() method in JavaScript is a higher-order function that reduces an array to a single value. reduce() takes a callback function as its first argument and an optional initial value as its second argument. For the callback function, it takes an accumulator as its first parameter (which contains the total value calculated from the previous iteration), and the value of the current element as its second parameter. When reduce() is run, the callback function iterates over every element in an array and applies the specified operation (like sum, subtraction, etc.) onto each one, then returns the result as a single value.
When should I use reduce?
The reduce() method in JavaScript can be used for data manipulation tasks like calculating the sum, product or average of elements in an array, flattening an array, finding the maximum and minimum value in an array, removing duplicate elements in an array and more.





