Sort By
Most Recent
28 Articles
A transistor is a semiconductor that amplifies or switches electronic signals. Transistors serve as the basic building blocks of modern electronics.
Nanotechnology is a field of science and engineering that focuses on the design and manufacture of extremely small devices and structures.
The Faraday constant is the electric charge per mole of electrons. It’s denoted by the symbol F and is a physical constant named after the British scientist Michael Faraday.
The dielectric constant (also known as relative permittivity) is a measure of a material’s ability to store electrical energy in an electric field.
An electrical charge is a fundamental physical property that will cause objects to attract or repel one another.
An EMP (electromagnetic pulse) is an intense burst of electromagnetic energy, usually caused by an abrupt acceleration of charged particles.
Activation functions help a neural network model complex relationships in the data but how (and when) do we use them, exactly?
A unit test is a functional test of an application’s smallest possible source code unit. The unit test aims to test the individual components of the software independent of other parts of the code.
You don’t need a crystal ball to tell the future. You can predict customers’ behavior using this deep learning technique.
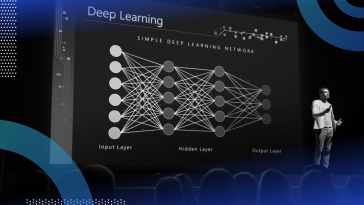
Deep learning uses multi-layered structures of algorithms called neural networks to draw similar conclusions as humans would. Here’s how it works.
In the final installment of this series, we’ll walk through stochastic policy gradients and AI agents in continuous action spaces.
In this step-by-step explanation of double deep Q-learning, I’ll show you how you can practice on your own.