Let’s say you receive an error message from Git Bash.
bash: pip: command not foundAnd an error message from DOS command line.
'pip' is not recognized as an internal or external command,
operable program or batch file.What do you do?
How to Check For and Install pip in Terminal
How to check if pip is installed on Windows and Mac: In Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on Mac, type and enter: pip --version. If pip version is shown then it is installed.
How to install pip on Windows and Mac: Type and enter "curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py" in Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on Mac.
After, for Windows, type and enter: python get-pip.py. For Mac, type and enter: python3 get-pip.py
What Is a ‘Pip: Command Not Found’ Error?
First things first: A “pip: command not found” error message occurs when pip, the standard package installer for Python, is not correctly installed on the system or added to the system’s PATH. Pip is included by default with Python 3.4 or later versions, so this error may occur if you have installed an earlier version of Python or haven’t added Python to your system PATH during installation. To fix this error, you will either need to re-install Python and check the box to add Python to your system PATH or install pip on your command line.
How to Fix ‘Pip: Command Not Found’ and Install Pip
First, make sure pip is installed on your system, as this may be the reason it is unable to be found.
If you’ve just installed Python, you may want to rerun your Python installer and make sure you check the box “Add Python to PATH.”
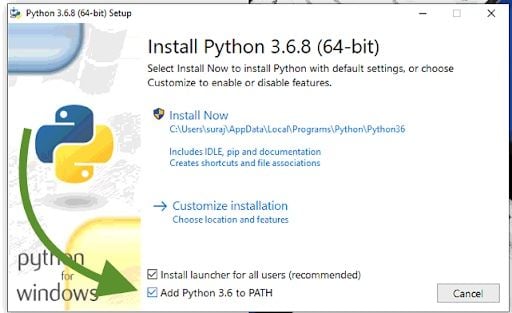
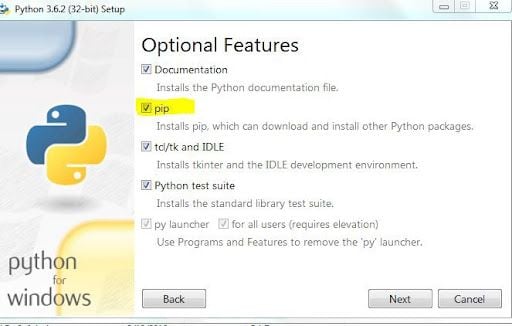
Next, click “Customize installation” and check the “pip” box under Optional Features.
Then, click “Next” to get to Advanced Options and check the “Add Python to environment variables” box. Adding Python to environment variables ensures that the Scripts folder with pip3.exe in it can be found.
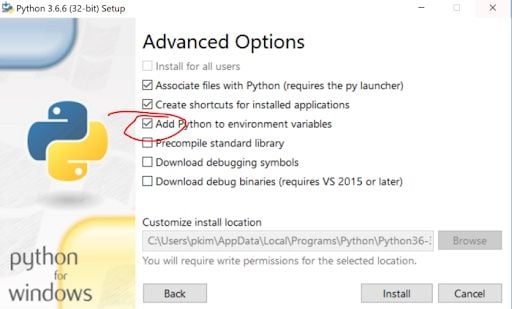
After checking the appropriate boxes, click “Install.”
Next, open your terminal in Windows and check for pip3.exe using the following command to ensure it’s downloaded on your computer:
C:\Users\YOUR_USERNAME\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\ScriptsNote that you can’t copy and paste that line. You will need to fill in your actual username and ensure the Python version number matches with the version you’re installing in that path. For example, since we’re installing Python version 3.6, it says “Python36” in its part of the path.
If you do find “pip 3,” you are in luck. It should look something like the image below.
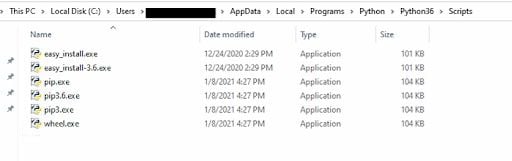
If you’re navigating on Windows, you can get to the AppData folder by typing the %appdata% macro into the path bar in a Windows File Explorer (formerly Windows Explorer) window.
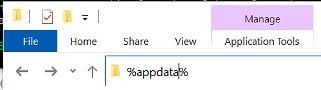
If you can’t find the pip3.exe, it might not be installed. So, check to see that you did install pip correctly. It’s easy to pass over these little things, and you may have missed it the first time through.
How to Add Pip to System PATH Using Command Line
If pip is installed but showing a “not on PATH” error, it must be added to Windows environment variables in order to be added to the system’s PATH. This is can be done if you use the Python official installer, but if you don’t want to run it again you can add pip to the system PATH using the command line.
It is also possible that you may have skipped over this warning right after summoning Python from the command line or after installation.
WARNING: The scripts pip.exe, pip3.6.exe and pip3.exe are installed in 'C:\Users\YOUR_USERNAME\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\Scripts' which is not on PATH.
Consider adding this directory to PATH or, if you prefer to suppress this warning, use --no-warn-script-location.It’s easy to miss, and I think developers get into the habit of ignoring warnings like this because code often compiles with thousands of compiler warnings.
1. Search “Environment” on Windows and Click “Edit the system environment variables”
Now, let’s edit your path. Start by searching for “environment” in your Windows search tab.
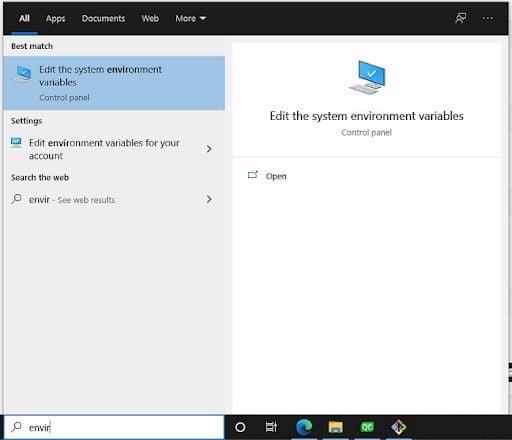
Then select, “Edit the system environment variables.”You will see a window like this below.
2. Click Environment Variables
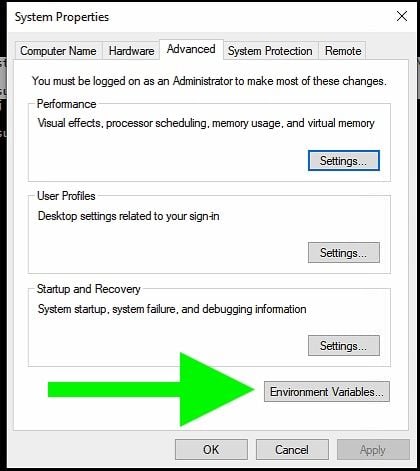
Click the button the green arrow is pointing to labeled “Environment Variables.”
3. Select the Path Variable Under System Variables
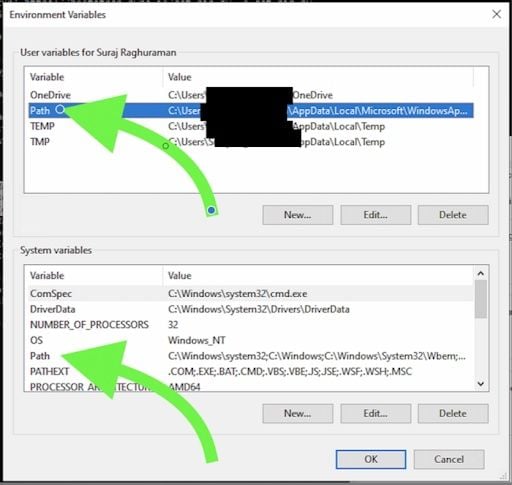
You will then have a choice. You can either edit the user path or the system path.
I usually edit the system path and have never run into issues. However, I suspect that the safer thing to do, the more “principle-of-least-privilege” thing to do, would be to edit the user path. That way only the user who needs pip access will have it. It’s up to you, but I typically never have more than one user on my machine. However, many workplaces do.
4. Click Edit for the Selected Path
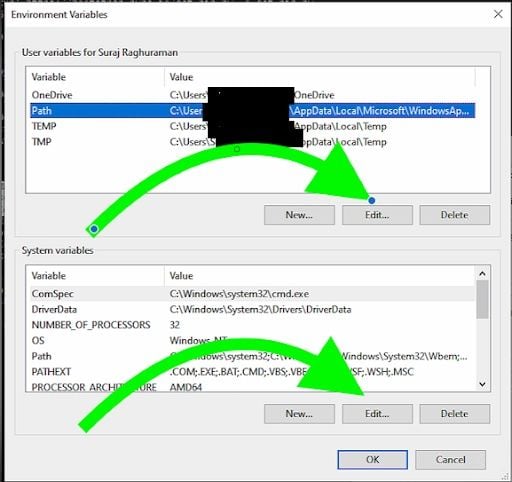
After selecting your path variable, click “Edit.”
5. Click New and Paste the Path Line With Your Username
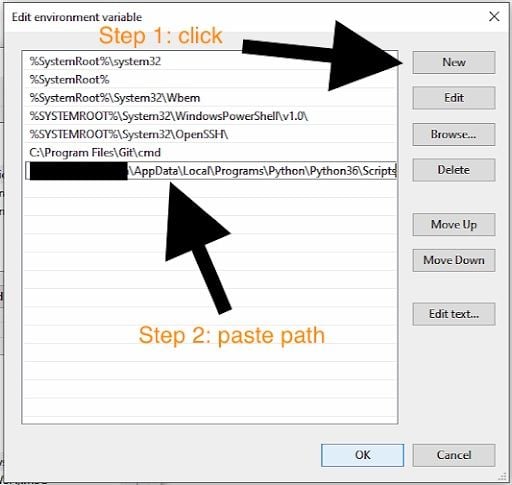
From here, you’ll want to copy the path we discussed earlier into the new line.
C:\Users\YOUR_USERNAME\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\ScriptsMake sure you use your actual username in the place of YOUR_USERNAME, and that the Python version number matches the version you installed. Remember, you can’t just copy paste it. While you’re here, it’s also not a bad idea to add Python to your path. So, add this folder, too. It’s just one level up:
C:\Users\YOUR_USERNAME\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36\If you can’t open the path in File Explorer, it’s not a real path.
6. Click OK After Pasting Path
Once you’ve pasted in the new path to the end of the path system environment variable, you can click OK to close the window.
7. Restart Terminal and Type ‘pip’ to Check Installation
Next you need to restart the command line terminal, and type in “pip” to check your work. If it works, you should see the help output in the terminal. It should look something like the image below.
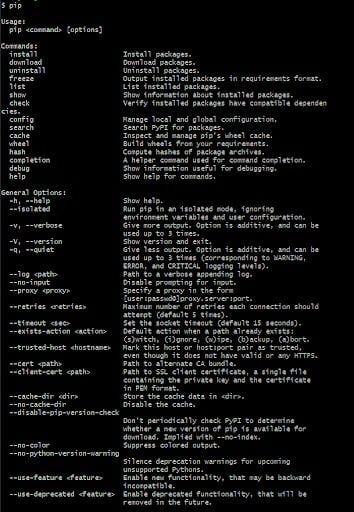
If you don’t see it, you should go back to your path environment variable and make sure it is correct. Watch out for spaces in the wrong place, extra characters, etc.
The example path I gave you is on the C:/ drive. If you installed pip and Python to a different drive, use that one instead.
8. Optional: Update Pip PATH Variable Using Bash
Alternatively, you could do this in your ~/.bashrc file for Git Bash.
Enter, vim ~/.bashrc to open the bashrc file. This is a file that executes every time you open a shell window. You’ll have to re-open your shell to get the changes that you make to the bashrc file.
alias pip='C:\\Users\\YOUR_USERNAME\\AppData\\Local\\Programs\\Python\\Python36\\pip3.exe'A few other things to note:
- You MUST use single quotes as double quotes will not work.
- You MUST escape your \ slashes.
- You MUST use Windows style slashes (\). Unix style (/) will not work.
- You MUST escape your spaces in the path. If YOUR_USERNAME has a space you would enter the following:
alias pip='C:\\Users\\YOUR\ USERNAME\\AppData\\Local\\Programs\\Python\\Python36\\Scripts\\pip3.exe'
This can be handy if you don’t think you should edit the path. There’s more than one way to crack an egg. Creating an alias will just make pip automatically call that pip3.exe you pointed it to. However, you may need to add the “Scripts” folder to the path in order to find some modules you installed.
On Windows especially, it seems to nearly always be safe to append to the path. But I always do that little trick to make sure I have an alias around just in case.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to fix pip not found?
To fix a “pip: command not found” error, make sure pip is installed and added to your system’s PATH. This can be done by downloading the latest version of Python and checking the “Add Python to PATH” box, the “pip” box (under Optional Features) and the “Add Python to environment variables” box (under Advanced Options) in the Python installer. Pip can also be installed and added to a system PATH manually using command line.
How to install pip command in Python?
Pip can be installed in Python on Windows by using the get-pip.py command directly in command line.
First, download get-pip.py. Then to install pip, use the command:
python get-pip.py
Why don't I have pip in Python?
Pip is only included with Python 3.4 and later versions, and must have the “Add Python to PATH” box, “pip” box and “Add Python to environment variables” box checked during installation to be recognized by the system and used with Python.





