Bias, “the prejudice or unsupported judgments in favor of or against one thing, person or group as compared to another, in a way that is usually considered unfair,” affects us all in one way or the other. One of the most prominent examples of unconscious bias we all experience regularly is in companies’ hiring processes. Often, job descriptions contain elements that favor a particular gender, race, physical or cognitive ability — in ways we might not even recognize.
Biased job descriptions not only limit the candidate pool but also diversity in the workplace. Therefore, companies need to check for (and eliminate) unconscious bias in job descriptions to foster a healthy, equitable and diverse company culture. But how?
Need to Spot Unconscious Bias in Job Descriptions? Get H2O Wave.
How AI Can Flag Bias in Job Descriptions
Machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies have made it possible to analyze data from various sources accurately and precisely. Using structured or unstructured data, AI-backed technologies can provide superior results compared to manual processing. However, it’s essential to keep in mind that the end users of these tools will not always be people with a background in software engineering or machine learning. To make such tools mainstream, it’s crucial to make them more accessible. We need AI applications that are infused into platforms and enable business users to directly interact with data without interacting with code.
Well, H2O Wave has been created to address this very issue. I’ll show you how it works.
What Is H2O Wave?
H2O Wave is an open-source Python development framework that helps data scientists, machine learning engineers and software developers to develop real-time interactive AI apps with sophisticated visualizations. You can create interactive and visual AI applications with just Python — HTML, CSS and Javascript skills aren’t required. The Wave apps run natively on Linux, Mac and Windows,
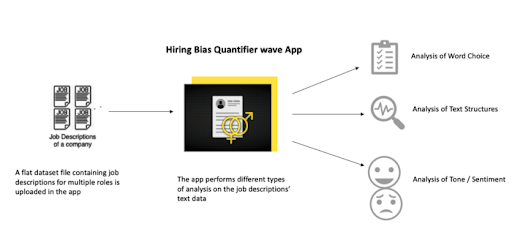
In this article, we’ll create a hiring bias quantifier using the H2O Wave toolkit to analyze job descriptions for potential bias. The target audience for this app includes business analysts, data scientists and human resource personnel.
Hiring Bias Quantifier
The hiring bias quantifier uses text and statistical analysis to measure and quantify unconscious bias in job descriptions. Specifically, this application summarizes different types of analyses that measure, quantify and analyze gender bias. The hiring bias quantifier produces several valuable insights to help us understand how much bias exists in job descriptions and compares the job description with a benchmark.
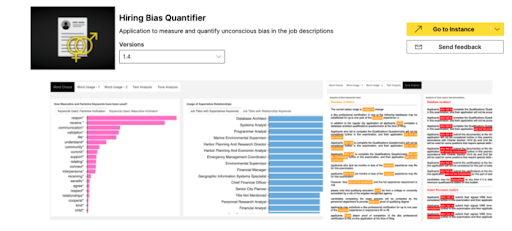
Hiring Bias Quantifier App
Let’s now see how this app can help us detect unconscious bias in a data set containing job descriptions. In this article, we’ll with a preprocessed version of the Los Angeles Job Description data set from Kaggle, which includes the following attributes:
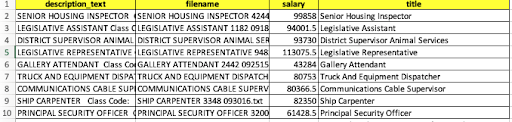
Our job is to detect whether the text in the description_text column contains unconscious bias or not.
Methodology
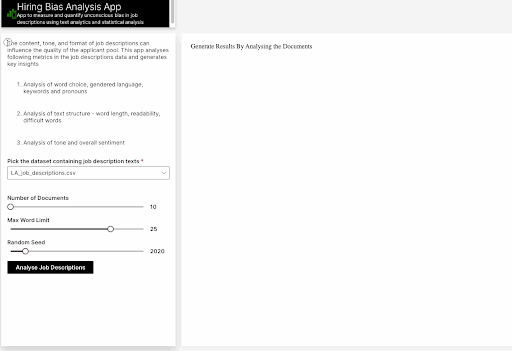
First, we load the data set into the app. The hiring bias quantifier consists of several machine learning algorithms and models that analyze different parts of the job description text and perform analysis based on the word choice, text structure, tone, sentiment, etc. The app generates a detailed report containing multiple insights compiled into a dashboard.
3 Types of Analysis by the H2O Hiring Bias Quantifier
- Analysis of Word Choice
- Analysis of Text Structures
- Analysis of ton/Sentiment
Here are some of the detailed results:
1. Analysis of Word Choice
Unconscious bias in job descriptions towards a specific gender can limit the candidate pool and overall staff diversity. The figure below shows how the choice of particular words can lead to bias.
Use of Gendered Keywords in Job Descriptions
Using gendered language in job descriptions can discourage certain people from applying to those jobs. For example, words deemed more “aggressive,” “assertive,” or “independent” typically discourage women from applying to specific roles. The plots below show the stereotypically masculine and feminine keywords identified in the data set.
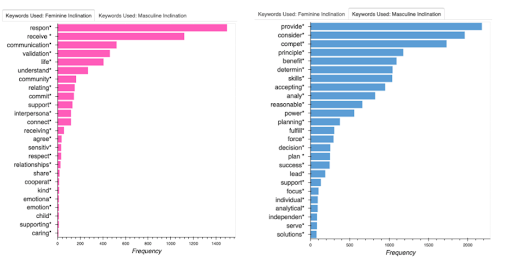
Distribution of Masculine/Feminine Associated Keywords
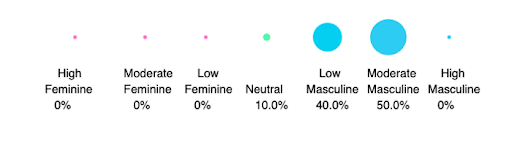
For the current pool of job descriptions, analysis shows these job descriptions are most likely going to attract masculine applicants.
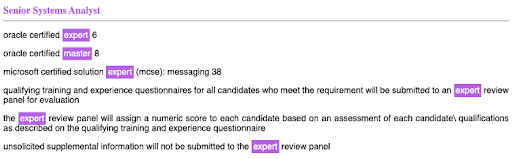
Superlatives
The following example shows certain job descriptions where we see more superlative keywords, specifically “master” and “expert.” These keywords have a latent masculine associations and show a preference towards a particular gender.
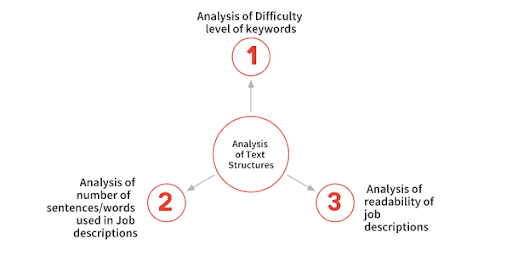
2. Analysis of Text Structures
Several studies (like those on LinkedIn, Forbes, and Glassdoor) suggest that how a job description is written can significantly influence both the quality and the quantity of an applicant pool.
On the other hand, a description lacking vital features (for example — an optimal word count, choice of the words, overall tone) may attract fewer candidates.
The text structure of a job description can be analyzed in several ways, namely:
Keyword Difficulty Level
Since readability is of paramount importance, it’s important to focus on choosing words that aren’t overly and needlessly complex. The graph below shows the high usage of difficult words in the descriptions of various job postings.
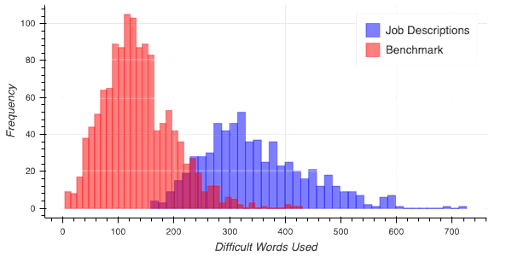
Readability
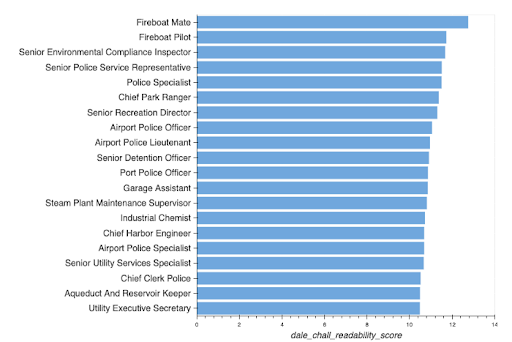
Similarly, companies should refrain from making job descriptions too complex or challenging to read, which could (for example) limit your applicants who are non-native speakers of that particular language. Analysis found that job descriptions for the following posts were the least readable.
3. Analysis of Tone and Sentiment
Sentiment analysis is a subfield of natural language processing (NLP) that identifies and extracts opinions from a given text. Sentiment analysis of job descriptions can help the companies gauge their tone. The sentiments or the tone conveyed in the job descriptions should not be too negative or demanding, which results in fewer applicants for the job — especially applicants from underrepresented groups.
Use of sentences and words that convey moderate or high negative sentiments should be avoided. Companies must ensure the tone of the job descriptions shouldn’t be too negative or they risk scaring away viable (though potentially less experience) candidates. For instance, keywords containing negative sentiments that have been automatically highlighted below should be avoided.

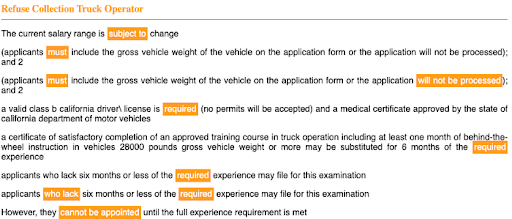
Strict Keywords
Again, excessive use of demanding keywords is also not desirable in a job description. Phrases such as “who fail,” “will not be considered,” “must-have,” etc., should be avoided or replaced with positive and encouraging words like “good to have,” “add-on,” etc. in order to attract a diverse pool of candidates.
The Takeaway
The point of a job description is to encourage a diverse group of people to apply. The choice of language and words you use in your job descriptions plays a major role in promoting applicant diversity. Hence, factors like content, tone, language and format can directly (or indirectly) influence a company's hiring process but these trends can be difficult for a human reader to spot efficiently. AI-powered software like H2O Wave is a great way to root out unconscious bias in your job descriptions and diversify your applicant pool.





